Getting Started Guide: SNMP Polling
This guide will walk you through the process of configuring SNMP polling in NetFlow Optimizer. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) complements NetFlow data by providing detailed device-level metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and interface status. This combined view of flow data and device health gives you a comprehensive understanding of your network's performance.
Why SNMP Polling?
NetFlow provides valuable insights into network traffic flow, showing who is talking to whom and how much data is being transferred. However, it doesn't always reveal why performance issues might be occurring. SNMP polling fills this gap by collecting vital device statistics. For example, high bandwidth usage on a link might be due to legitimate traffic, or it could be caused by a failing interface. SNMP data can help you quickly pinpoint the root cause.
Introduction to SNMP Monitoring in NFO
NFO leverages the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to collect vital performance data, network details, and alerts from your devices. As part of your current NFO license, you are entitled to SNMP Basic, which offers foundational monitoring to complement your NetFlow visibility.
For advanced security, automation, and large-scale management, we offer the SNMP Pro tier. Before proceeding with configuration, please review the capabilities included with your current license level below.
| Capability | SNMP Basic (Included with NetFlow License) | SNMP Pro (Paid Tier) |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Support | SNMPv2c | SNMPv2c & SNMPv3 |
| Secure Polling/Traps | No (v2c is clear-text) | Full Encryption & Authentication |
| Device Configuration | Manual device entry only | Automated Discovery |
| Management | Individual device lists only | Device Grouping |
| Trap Management | Receive Traps (SNMPv2c) | Receive Traps (SNMPv2c & SNMPv3) |
If your environment requires secure SNMPv3 protocol support, automated device discovery, or centralized management via Device Groups, you will need to have the SNMP Pro license.
Planning
Device Groups and Vendor-Specific OIDs
In networks with devices from multiple vendors (Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, Juniper, etc.), a significant challenge arises: different vendors often use different Object Identifiers (OIDs) to represent the same information (e.g., CPU utilization, memory usage). Polling all devices with a single, generic set of OIDs would lead to:
- Inefficiency: Many OIDs would be irrelevant to certain device types, resulting in unnecessary polling and wasted resources.
- Inaccurate Data: Attempting to use vendor-specific OIDs on devices that don't support them would result in errors or time-outs.
Device groups solve this problem by allowing you to organize your devices based on vendor or type and assign specific OID sets to each group.
How Device Groups Work
-
Create Device Groups:
- In NetFlow Optimizer, device groups are automatically created with auto-discovery as vendor names, or you can create device group manually (e.g., "Cisco Routers," "Palo Alto Firewalls," "Juniper Switches").
- This grouping can be based on vendor, device type, or any other logical criteria that suits your network.
-
Assign Devices to Groups:
- Add your devices to the appropriate device groups.
- This ensures that each device is associated with the correct set of OIDs.
-
Configure OID Sets for Each Group:
- For each device group, define a set of OIDs that are specific to the devices in that group.
- For example, the "Cisco Routers" group would have OIDs for Cisco-specific CPU and memory utilization, while the "Palo Alto Firewalls" group would have OIDs for Palo Alto Networks-specific metrics.
- This is the most important step. Consult your vendor documentation for the correct OIDs.
-
Polling Based on Groups:
- NetFlow Optimizer will then poll each device using the OID set that is assigned to its group.
- This ensures that each device is polled with the correct OIDs, resulting in accurate and efficient data collection.
Benefits of Using Device Groups
- Accurate Data: Ensures that each device is polled with the correct OIDs, resulting in accurate data.
- Efficient Polling: Avoids unnecessary polling of irrelevant OIDs, reducing the load on both NetFlow Optimizer and the devices.
- Simplified Management: Makes it easier to manage SNMP polling in large and diverse networks.
- Vendor Specific Polling: Allows for the polling of vendor specific MIBs and OIDs.
Example Scenario
- You have a network with Cisco routers, Palo Alto firewalls, and Juniper switches.
- You create three device groups: "Cisco Routers," "Palo Alto Firewalls," and "Juniper Switches."
- You add your devices to the appropriate groups.
- You configure OID sets for each group, using the vendor-specific OIDs for CPU utilization, memory usage, and other relevant metrics.
- NetFlow Optimizer then polls each device using the OID set that is assigned to its group.
Important Considerations
- Maintain an updated list of vendor-specific OIDs.
- Regularly review and update your device groups and OID sets as your network changes.
- Test your OID sets on a test device before deploying to production.
By using device groups, you can ensure that your SNMP polling is accurate, efficient, and tailored to the specific needs of your network.
Prerequisites
- A working installation of NetFlow Optimizer.
- Network connectivity between NetFlow Optimizer and the devices you want to monitor.
- SNMP credentials (community strings for SNMPv2c, user/authentication details for SNMPv3) for the devices. We strongly recommend using SNMPv3 for enhanced security.
Steps
This guide describes how to use NetFlow Optimizer to perform SNMP polling from your devices and send this data in Syslog or JSON format to your monitoring system or SIEM. To start SNMP polling with NFO please follow the steps below:
- Configure NFO SNMP Management
- Enable and configure SNMP polling Modules
- Configure NFO output
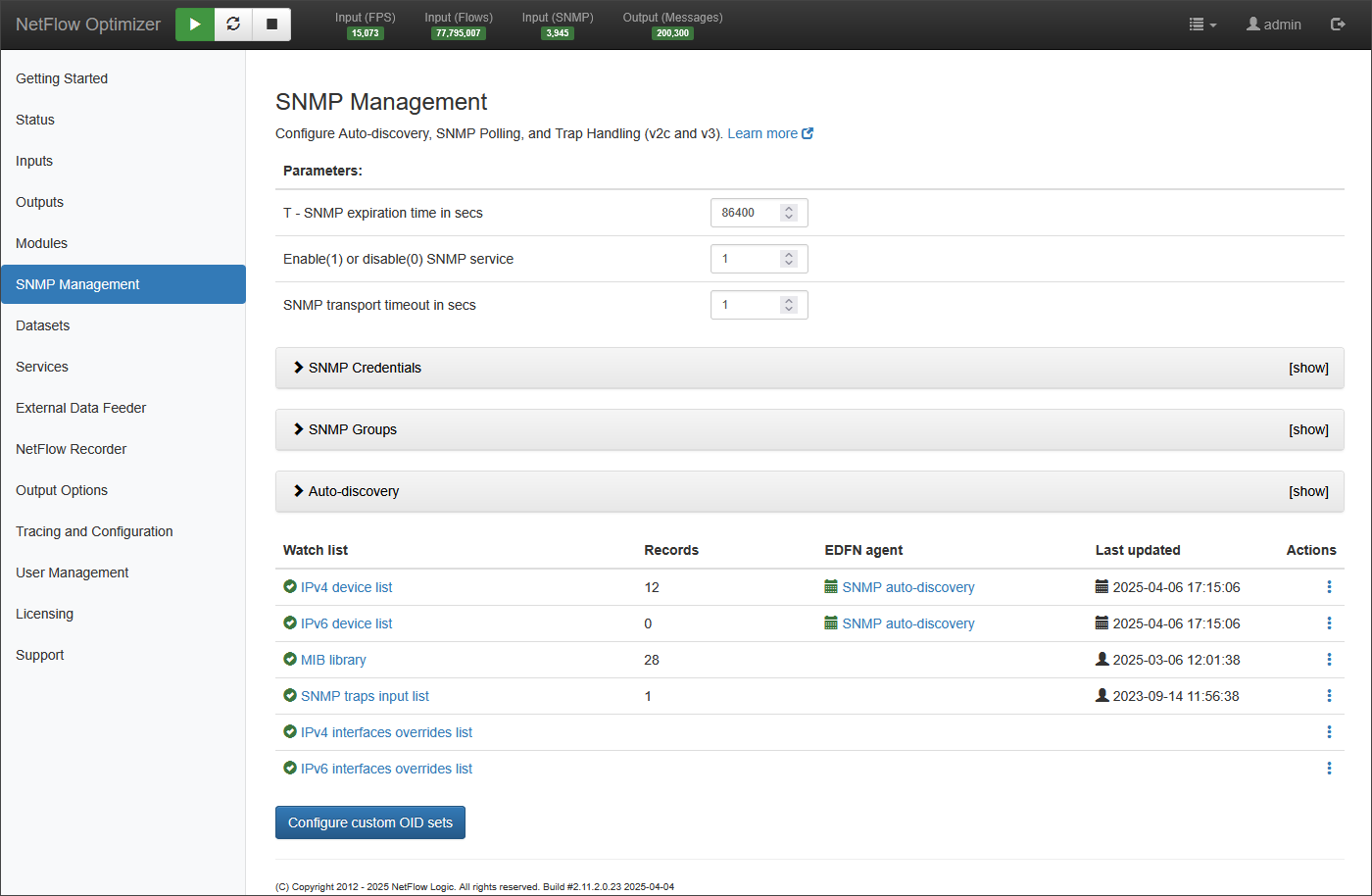
NFO provides built-in SNMP Management:
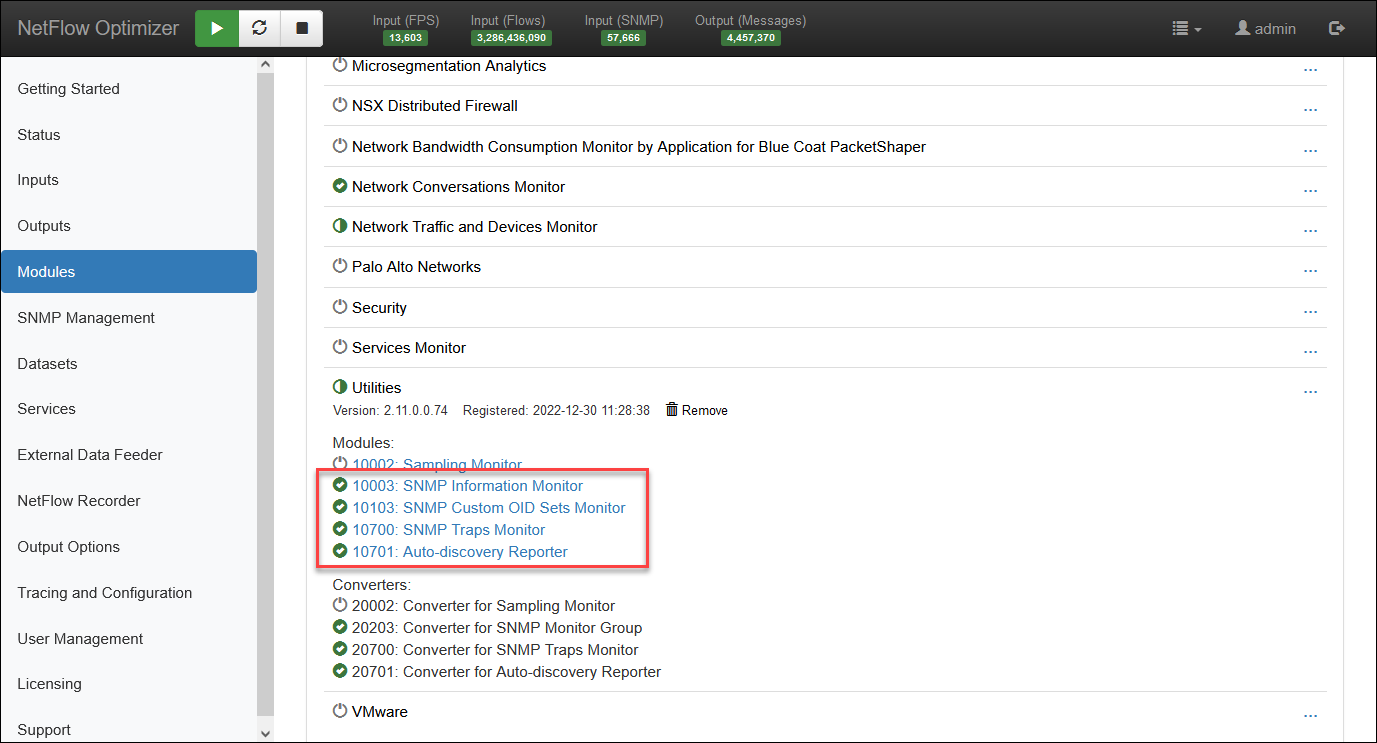
and several SNMP Modules:
Configure NFO SNMP Management
NFO SNMP Management configuration includes the following:
- Configure SNMP credentials
- Configure SNMP device groups
- Configure the list of devices to be polled, optionally using auto-discovery
- Optionally add SNMP MIBs to build custom OID sets
For more information about NFO SNMP Management, visit NFO Administration Guide SNMP Management section.
SNMP Credentials
SNMP polling typically requires authentication. NFO supports SNMP v2c community string authentication and SNMP v3 user-based authentication.
For more information about SNMP credentials setting, visit NFO Administration Guide SNMP Credentials section.
SNMP Groups
SNMP Groups in NetFlow Optimizer allow you to organize devices for SNMP polling. Grouping by vendor or type enables consistent polling configurations and simplifies management across multiple devices, ensuring uniform data collection and targeted analysis.
List of Devices
Now you need to create the list of devices to be polled. You can create this list by one of the following ways:
- Type comma-separated entries in this window
- Create a CSV file using the provided template and upload it
- Use the External Data Feeder Agent for NFO (EDFN) to update this list on the specified cron schedule:
- From a CSV file created by an external process
- and/or configure Auto-discovery
For details, visit Configuring Auto-Discovery Based on SNMP Polling.
MIB Library
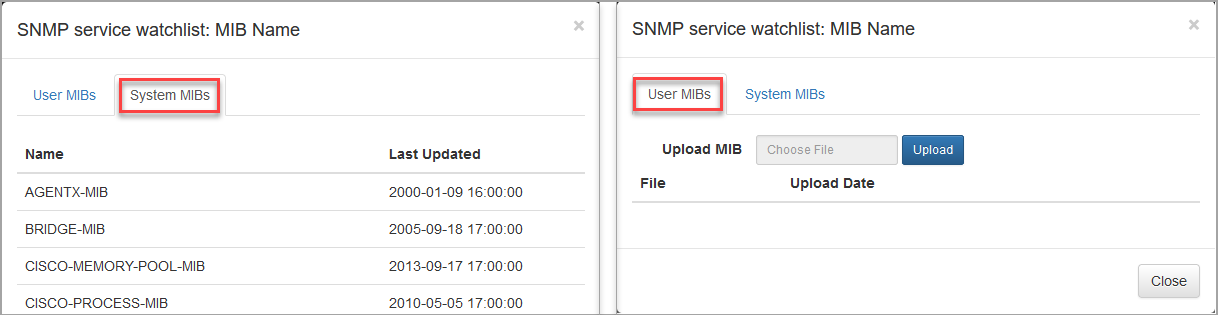
NetFlow Optimizer includes a number of pre-loaded SNMP Management Information Bases (MIBs), also known as Standard MIBs. These MIBs allow you to navigate the SNMP tree and build sets of OIDs for SNMP polling. If your OIDs or MIBs are not in the list of Standard MIBs, you can upload them using the User MIBs tab. Click on MIB library as shown below.
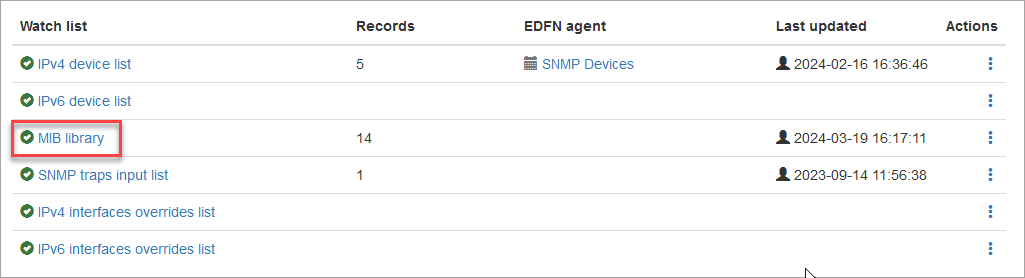
and upload your MIBs on User MIBs tab
SNMP traps input list
Specify the list of ports and credentials. This port and credentials are used by devices when sending SNMP traps to NFO.
For SNMP v3 make sure you specify Engine ID in Credentials
IPv4 and IPv6 Interfaces overrides
Use these lists if you need to override values returned by polling interface data, for example interfce speed - ifSpeed or interface name - ifName
SNMP Polling Modules
SNMP Information Monitor
This Module is designed to get information from network devices configured to send NetFlow data to NFO. SNMP OIDs in this Module are preconfigured. For a list of the preconfigured SNMP OIDs, visit SNMP Information Monitor section in NFO User Guide.
SNMP Custom OID Sets Monitor
This Module is designed to poll any OIDs from any device, regardless of whether the device is sending, or even incapable (e.g. printers, power supplies, etc.) of sending flow data. You can jump to this Module by clicking the Configure custom OID sets button.
You will be presented with the following screen.
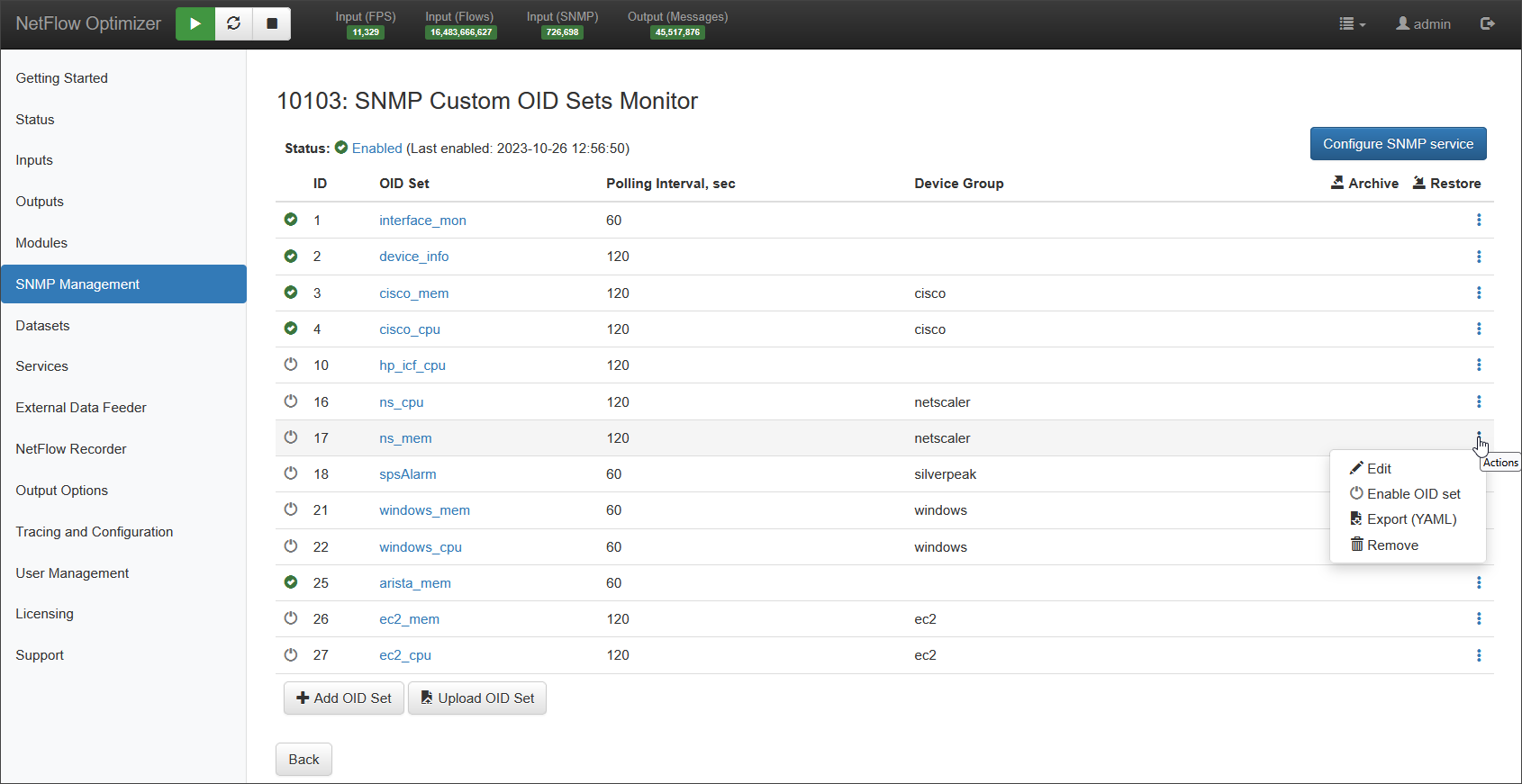
For details on confuring OID sets, visit SNMP Custom OID Sets Monitor.
Reporting OID Sets
The success of SNMP polling and the subsequent data collection heavily rely on the availability and responsiveness of the polled devices. Depending on the device status and the specific OIDs queried, the following outcomes may occur:
| Potential issues | Output |
|---|---|
| Device is unresponsive | None. Check unresponsive devices on the NFO Status>Logs page or in the log file nfo_audit.log |
| Requested OID is not supported by the device | The OID is not included in the output |
| OID is returned, but the value is null | "MISSING" |
| Returned value is not valid, e.g. wrong type, lenth, etc. | "na" |
NFO Output
For information about NFO Output configuration, visit Configure Outputs section in NFO Administration Guide.