SNMP Setup Guide
While NetFlow tells you who is talking, SNMP tells you why your network might be struggling. By combining flow data with device-level health metrics—like CPU, memory, and interface status—NFO provides a 360-degree view of your infrastructure.
NFO leverages the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to collect vital performance data, network details, and alerts from your devices. As part of your current NFO license, you are entitled to SNMP Basic, which offers foundational monitoring to complement your NetFlow visibility.
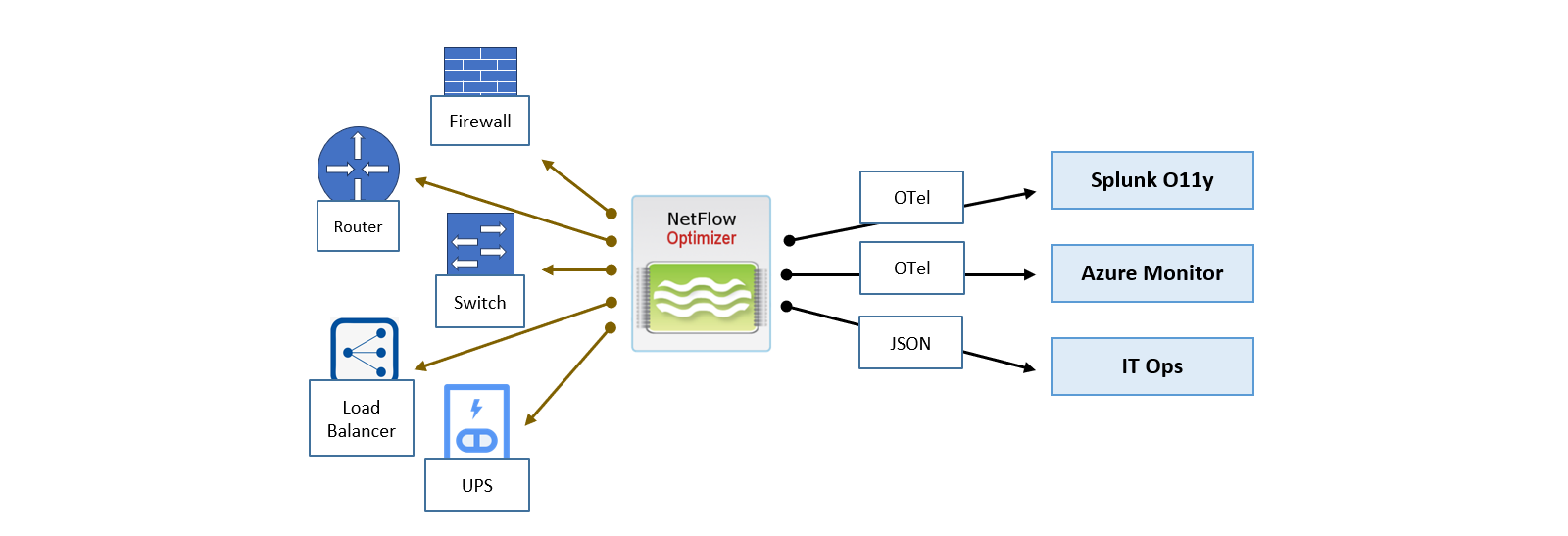
For advanced security, automation, and large-scale management, we offer the SNMP Pro tier. Before proceeding with configuration, please review the capabilities included with your current license level below.
| Capability | SNMP Basic (Included with NetFlow License) | SNMP Pro (Paid Tier) |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Support | SNMPv2c | SNMPv2c & SNMPv3 |
| Secure Polling/Traps | No (v2c is clear-text) | Full Encryption & Authentication |
| Device Configuration | Manual device entry only | Automated Discovery |
| Management | Individual device lists only | Device Classification |
| Trap Management | Receive Traps (SNMPv2c) | Receive Traps (SNMPv2c & SNMPv3) |
If your environment requires secure SNMPv3 protocol support, automated device discovery, or centralized management via Device Groups, you will need to have the SNMP Pro license.
The NFO Advantage: Autonomous Classification
NFO eliminates the manual burden of mapping thousands of Object Identifiers (OIDs). Our Autonomous Classification Engine automatically identifies your hardware, tags it by role (e.g., Firewall, Switch), and applies the correct vendor-specific OIDs immediately.
Step 1: Configure Credentials
Provide NFO with the "keys" to your network.
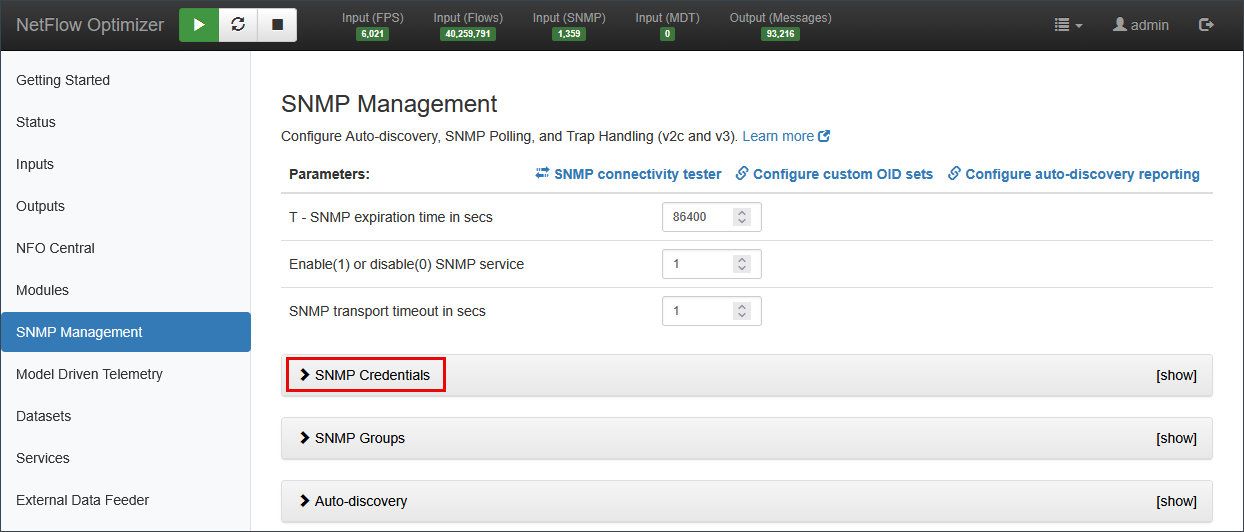
- Navigate to SNMP Management > Credentials.
- Add your SNMPv2c Community Strings or SNMPv3 Security Names.
- Click Save. NFO securely stores these for use during the discovery phase.
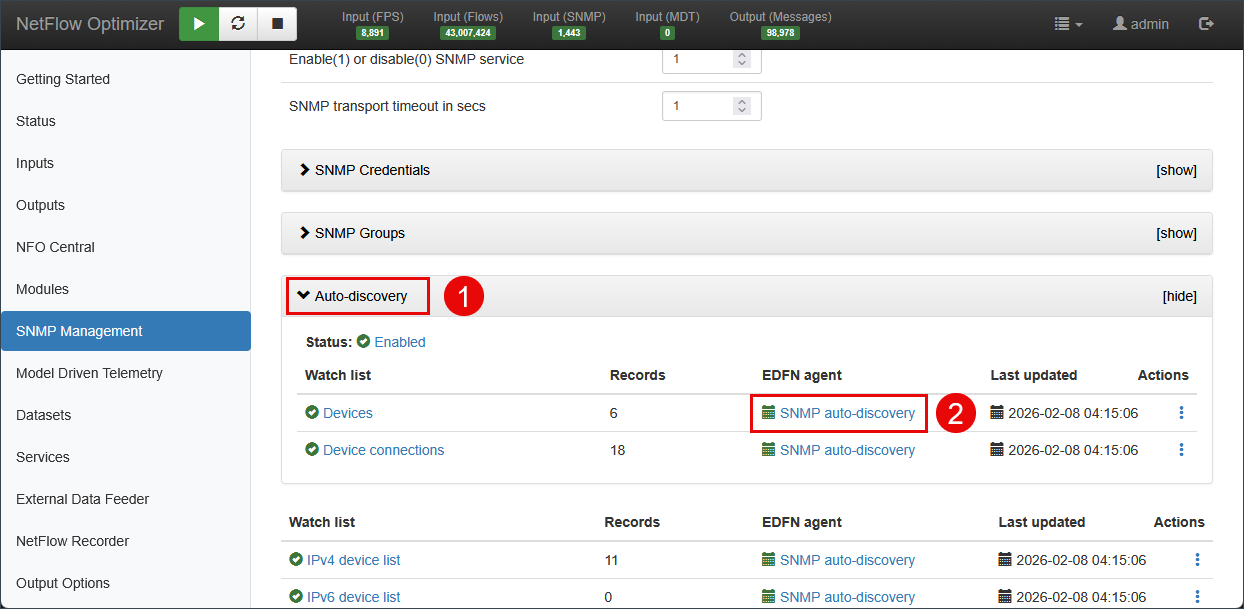
Step 2: Launch Auto-Discovery & Classification
NFO builds a dynamic inventory by probing your subnets or IP ranges and automatically identifying hardware types.
- Navigate to SNMP Management > Auto-discovery > SNMP auto-discovery tab.
- Define your IP Ranges on the
Auto-discovery networkstab (e.g.,10.0.0.0/24or192.168.20.1 - 192.168.20.24).
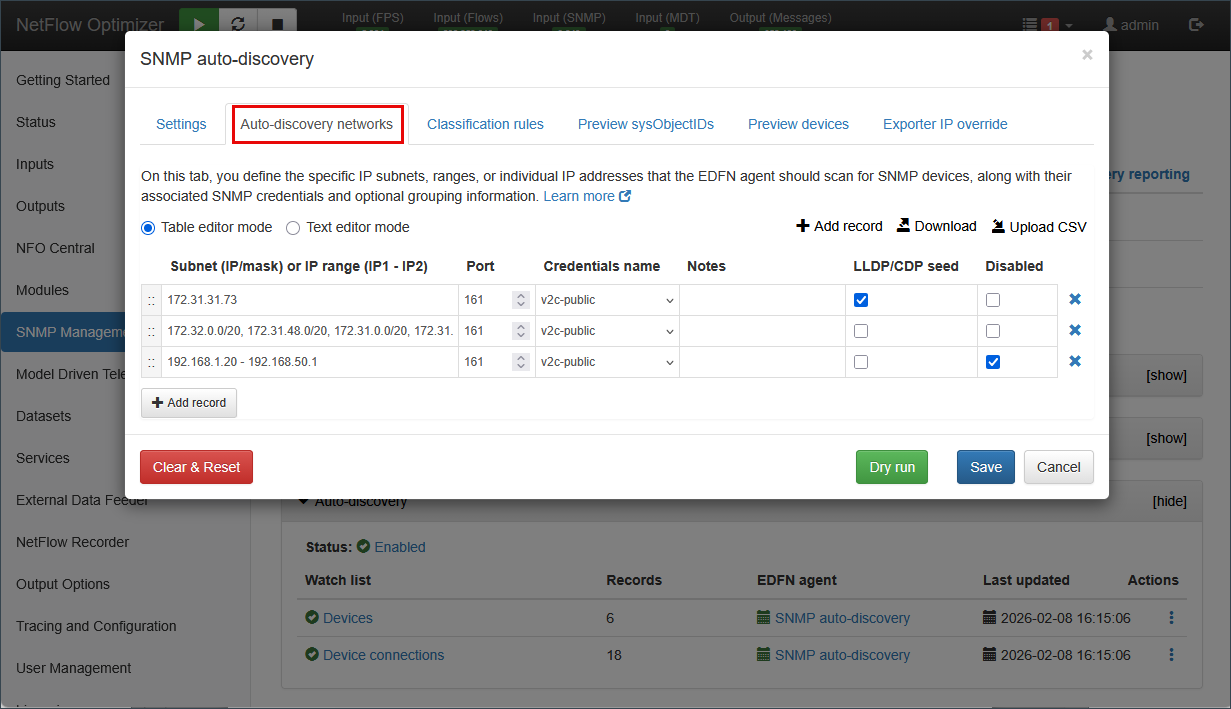
- Verify via Dry Run: Click Dry run. NFO will scan the range to identify hardware (Cisco, Juniper, Palo Alto, etc.). Switch to the
Preview devicestab to see how NFO has automatically mapped them to functional Device Groups.
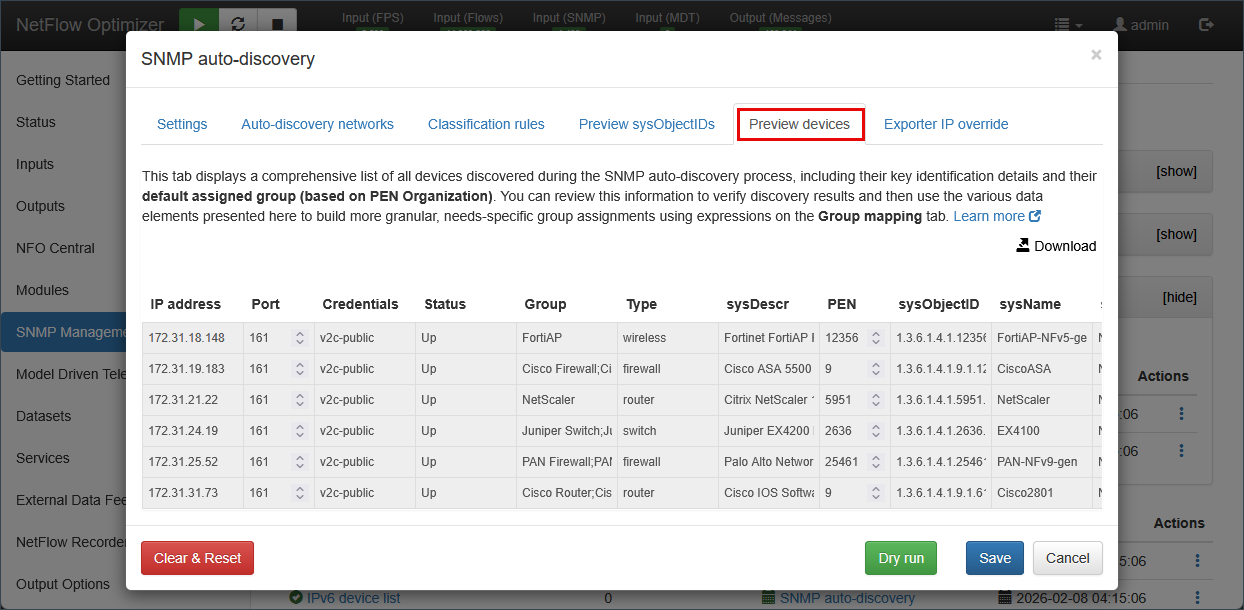
- Commit to Inventory: Once you are satisfied with the classification results, go to the
Settingstab and click Run now. This moves the discovered devices into your active monitoring inventory.
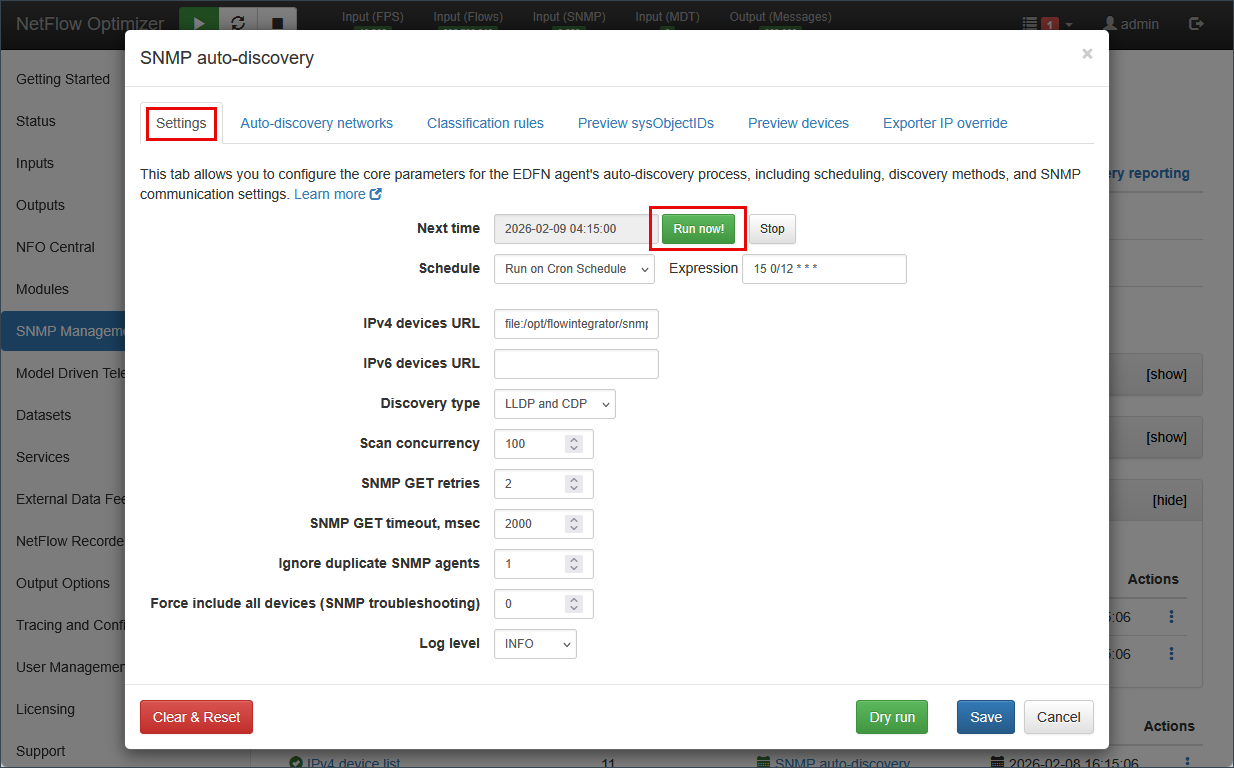
- Schedule Updates: Adjust the Cron schedule (default twice a day) to ensure NFO automatically detects and re-classifies new equipment added to your network.
For More Details For advanced configuration options—including excluding specific IP addresses, adjusting scan timeouts, or using LLDP/CDP for topology traversal—see the Auto-Discovery Configuration section in the EDFN Administration Guide.
Step 3: Enable the Collection Engine
Activate the logic that performs the actual polling.
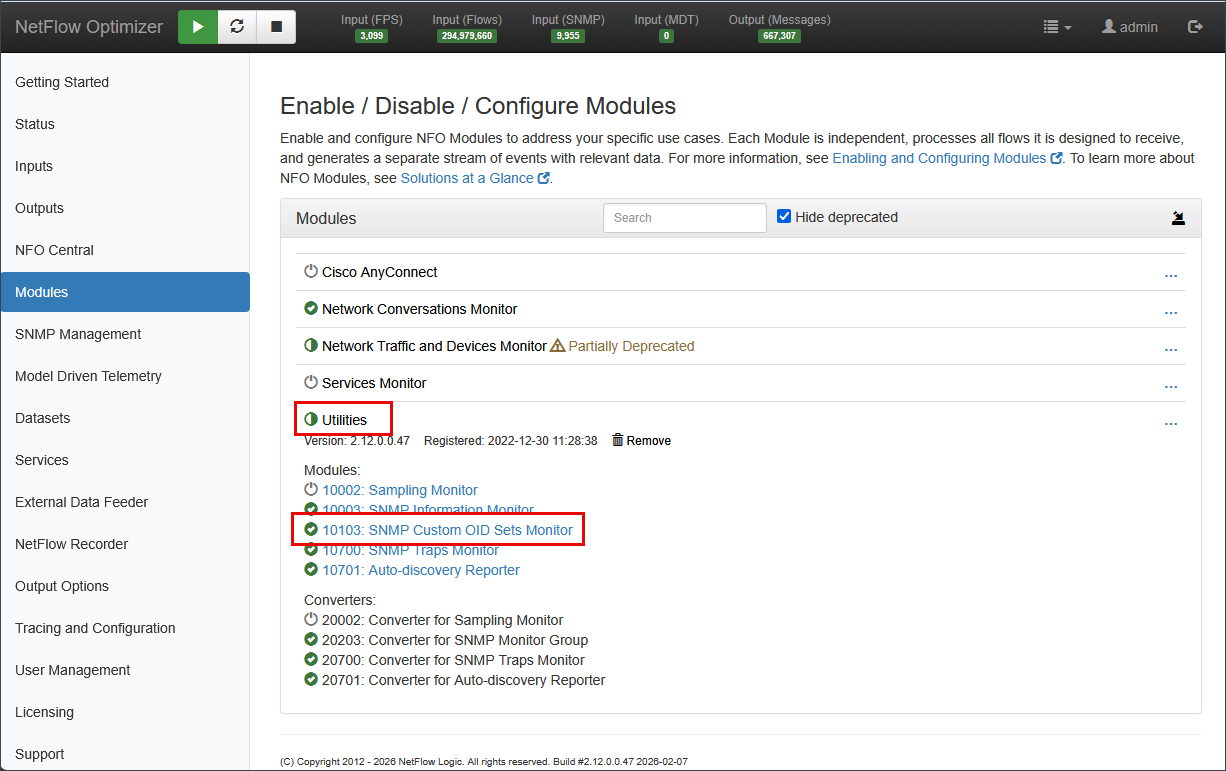
- Navigate to Modules > Utilities.
- Locate SNMP Custom OID Sets Monitor (10103).
- Toggle to Enabled.
- Toggle to Enabled the OID sets that correspond to your discovered Device Groups.
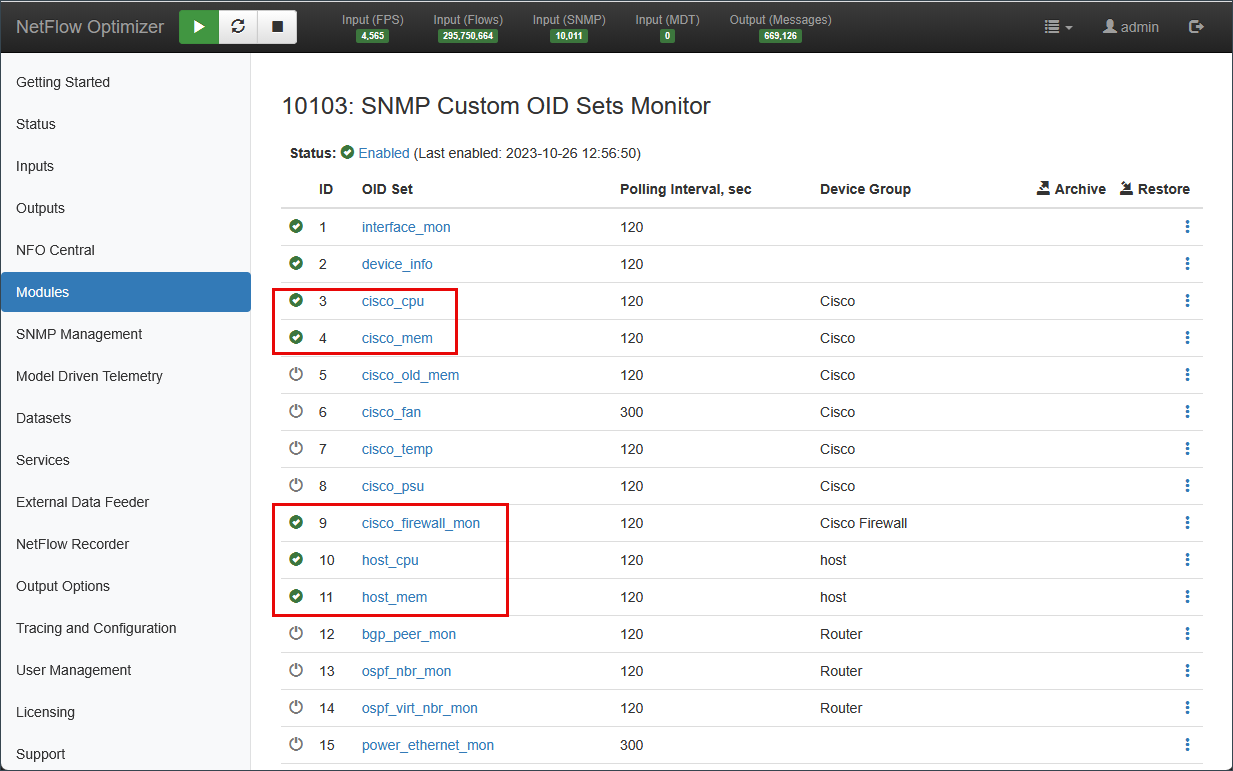
Result: NFO begins polling CPU, Memory, and Interface metrics based on the hardware it discovered in Step 2. No manual OID mapping required.
Understanding Multi-Group Inheritance
NFO doesn't just put a device in a folder; it applies layered intelligence. As devices respond, NFO analyzes system attributes (such as sysObjectID, sysDescription, and Private Enterprise Numbers) to classify them into multiple functional layers simultaneously. Unlike traditional systems that lock a device into a single folder, NFO uses Multi-Group Membership to tag assets by:
- Vendor & Model: (e.g., Cisco, Catalyst)
- Functional Roles: (e.g., Switching, Firewall)
- Feature Tags: (e.g., StackWise, VPN Gateway)
Verifying Health & Success
- The Device List: Navigate to SNMP Management > IPv4 Device List. Ensure your devices appear with their Type and Assigned Groups correctly identified.
- Polling Success: Check the NFO header for Skipped Requests. If this number is rising, check your firewall paths or verify that your community strings match the device configuration.
- Audit Logs: For troubleshooting, navigate to the Status page and select the Logs tab for a real-time view of system activity.
Next Steps
- Receive Alerts: Set up the SNMP Traps Input to ingest real-time hardware alerts.
- Customize Polling: Need to monitor a proprietary metric? See Creating Custom OID Sets.