SNMP Management
SNMP Service supports version SNMPv2C and SNMPv3, and includes:
- SNMP Polling
- SNMP Traps
- SNMP Auto-discovery
Before configuring the service, please review the feature breakdown below, as capabilities are determined by your NFO license level.
Feature Tiers and Protocol Access
Your NFO license determines the complexity and security of the SNMP features available to you. Before configuring the service, please review the feature breakdown below.
| Capability | SNMP Basic (Included with NetFlow License) | SNMP Pro (Paid Tier) |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Support | SNMPv2c | SNMPv2c & SNMPv3 |
| Authentication & Security | Clear-text Community String | Encryption & Authentication |
| Auto-Discovery | Manual device entry only | Automated IP Range Scanning |
| Device Grouping | Individual device lists only | Multi-Group Inheritance & Layered Monitoring |
| Custom OID Sets | Limited to Standard MIB-II | User MIBs & Custom OID Sets |
The ability to select SNMPv3 in the SNMP Credentials section, and the subsequent configuration of secure user-based authentication, is a feature exclusive to the SNMP Pro license. SNMP Pro is required for environments demanding data security and compliance.
Understanding the Classification Hierarchy
NetFlow Optimizer uses a two-tier Multi-Group Classification system. Instead of a single static assignment, devices inherit intelligence from multiple groups simultaneously to build a comprehensive monitoring profile. This hierarchy allows for both vendor-specific technical accuracy and role-based operational reporting.
Device Groups (Vendor, Role, & Features)
A Device Group identifies the "What"—the manufacturer, the product line, and the specific capabilities of the hardware. This is the technical layer of NFO.
- Purpose: Determines the technical monitoring profile. It tells NFO which vendor-specific MIBs, OIDs, or YANG models (for Model-Driven Telemetry) to use for data collection.
- Multi-Group Logic: A single device can belong to several groups at once to inherit layered intelligence.
- Examples: * Vendor & Model:
Cisco,Catalyst 9000 - Functional Role:
Firewall,Switching - Feature Tags:
StackWise,VPN Gateway
Device Types (Visualization & Orchestration)
A Device Type identifies the "How"—the primary category used to organize your data globally. This is the operational layer of NFO.
- Purpose: Used exclusively to organize visualizations, dashboards, KPIs, and alerts. It enables unified reporting across different vendors (e.g., an "All Firewalls" alert policy that covers both Cisco and Palo Alto).
- Logic: While a device can have many Groups, it is assigned a primary Device Type to anchor it within the UI and reporting engine.
- Examples:
firewall,router,switch,wireless,infrastructure(UPS/PDU/Printer).
Summary: Intelligence vs. Visualization
| Attribute | Device Group | Device Type |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Technical Intelligence | Operational Visualization |
| Function | Maps OIDs, MIBs, and YANG models | Organizes Dashboards, KPIs, and Alerts |
| Membership | Multi-Group (Inherits from many) | Single Category (Standardizes view) |
The Result: Your Device Groups ensure NFO is polling the right data, while the Device Type ensures that data is easy to find, alert on, and analyze in your dashboards.
Classification Rules
While NFO provides extensive built-in logic to handle this hierarchy automatically, administrators can use the Classification Rules tab to create overrides. This is useful for:
- Custom Tagging: Re-classifying a specific Linux server as a "Security Appliance."
- Organizational Logic: Moving devices into groups based on custom
sysNamepatterns (e.g., all devices with "NY-CORE" in the name).
SNMP Service Configuration Parameters
The SNMP service is enabled by default, and you can disable it if not needed.
To configure SNMP polling navigate to SNMP Management in the NFO web interface.
The service has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| T – SNMP expiration time in secs | Expiration time of SNMP data held in cache, default is 86400 seconds (1day) |
| Enable(1) or disable(0) SNMP service | 1 - SNMP service enabled; 0 - SNMP service disabled |
| SNMP transport timeout in sec | Time to wait for SNMP reply from network devices to polling requests |
The following image highlights the key parameters and sections within the SNMP Management interface, where you configure NetFlow Optimizer's interaction with network devices via SNMP for polling, trap handling, and auto-discovery. Refer to the numbered steps in the image and their corresponding descriptions below for details on each element.
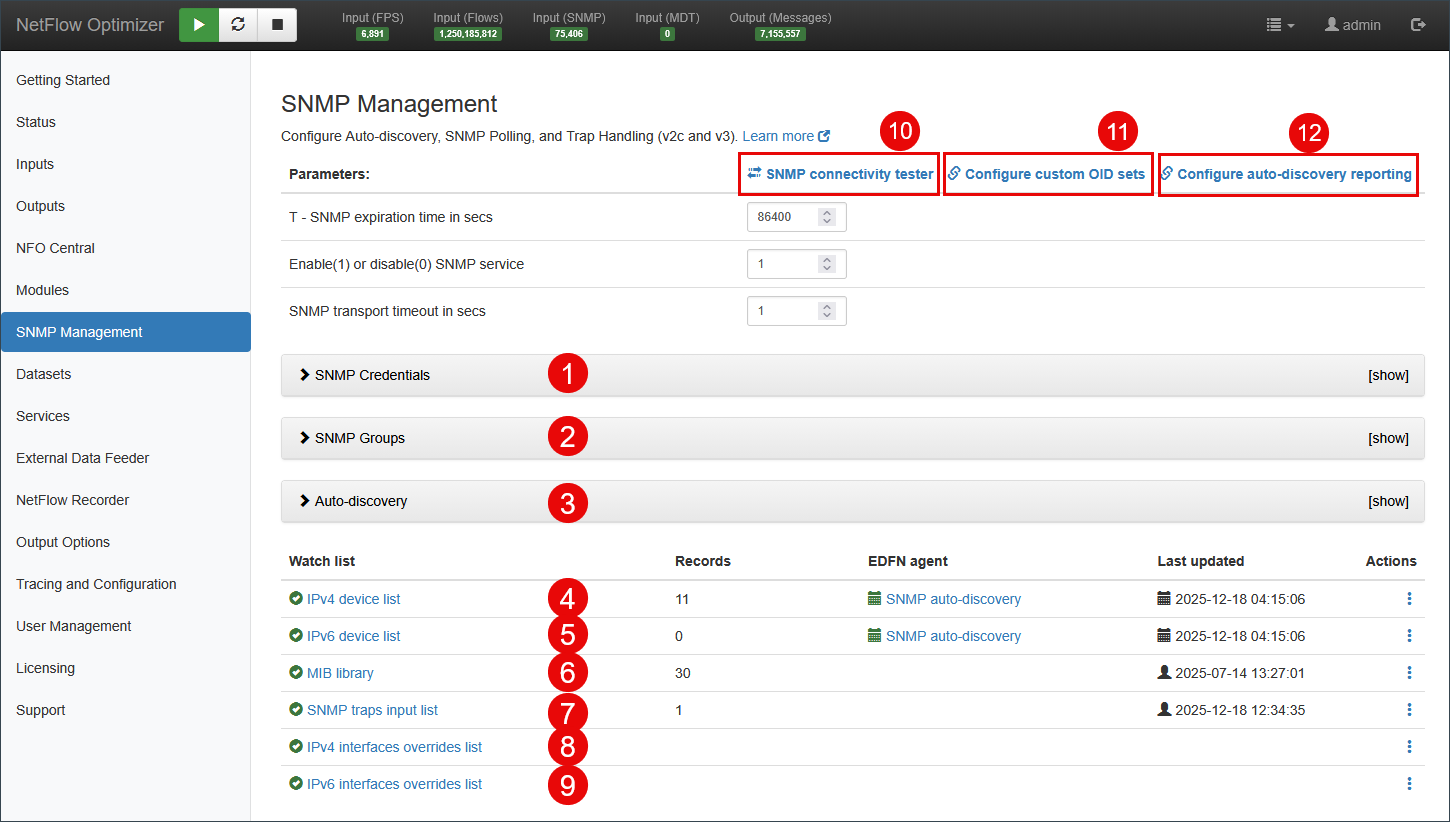
- SNMP Credentials: Authentication credentials for SNMP polling
- SNMP Groups: Settings for SNMP device groups
- Auto-discovery: Settings for SNMP-based autodiscovery, such as IP ranges, device groups, and other parameters
- IPv4 device list: The list of IPv4 devices to be polled, including mapping to exporter IP in case you receive flow data from these devices
- IPv6 device list: The list of IPv6 devices to be polled, including mapping to exporter IP in case you receive flow data from these devices
- MIB library: Optionally add MIBs not included in NFO to build OID sets
- SNMP traps input list: SNMP Trap ports and credentials
- IPv4 interfaces overrides list: SNMP Polling data defaults / overrides for IPv4 interfaces
- IPv6 interfaces overrides list: SNMP Polling data defaults / overrides for IPv6 interfaces
- Link to SNMP connectivity tested: Opens a pop-up to test SNMP connectivity using IP address and credentials
- Link to Custom OID Sets: Takes you to Custom OID Sets Monitor Module for SNMP metrics configuration
- Link to Auto-discovery Reporter: Takes you to Auto-discovery Reporter Module to configure reporting of discovered devices and connections.
SNMP Polling Configuration Steps
To ensure comprehensive visibility and accurate data collection, follow these steps to configure the SNMP service:
- Create SNMP Credentials: Define SNMPv2c community strings or SNMPv3 user-based authentication.
- Configure Auto-Discovery: Define the network ranges for scanning. NFO will populate the device list and automatically perform initial classification.
- Review and Override Classifications (Optional): Navigate to the Classification Rules tab. Review the Device Groups and Device Type assigned to your infrastructure. If a device requires a specific role change (e.g., a multi-purpose layer-3 switch that you want to classify strictly as a
router), create a custom rule to override the default logic. - Configure Auto-Discovery Reporting: Enable the Auto-discovery Reporter (Module 10701) to send discovery metadata to your SIEM for topology mapping.
- Assign Custom OID Sets: If you have specialized hardware (e.g., environmental sensors or proprietary appliances), define specific metrics in the Custom OID Sets Monitor (Module 10103) and link them to your custom groups.
SNMP Credentials
SNMP polling typically requires authentication. NFO supports SNMP v2c community string authentication and SNMP v3 user-based authentication. You can add an unlimited number of credential entries to support diverse network environments.
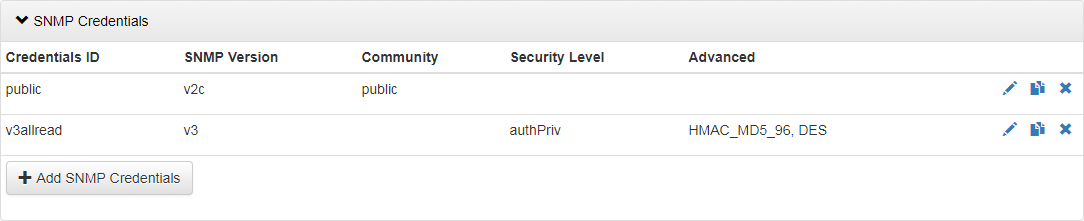
Click on “> SNMP Credetials” to setup SNMP authentications, and press Add SNMP Credentials button.
Adding SNMPv2c Credentials
For legacy environments or isolated networks where performance is prioritized over high security, use SNMPv2c:
- Community String: The read-only community string (e.g.,
public) used by the device.
Adding SNMPv3 Credentials
SNMPv3 provides commercial-grade security, including authentication and privacy (encryption). This feature requires an SNMP Pro license.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Security Level | Choose between noAuthNoPriv (no security), authNoPriv (authentication only), or authPriv (authentication and privacy/encryption). |
| User Name | The username provided for authentication on the network device. |
| Authentication Protocol | Supported protocols include MD5 and SHA. Newer versions may support advanced SHA variants (e.g., SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, and SHA512). |
| Authentication Password | The secret key or password used for authentication. |
| Privacy Protocol | The encryption standard for the data payload. Supported algorithms include DES and AES (including AES/192/192C/256/256C). |
| Privacy Password | The secret encryption key for the user. |
| Engine ID | (Optional) Specify the unique Engine ID for the device if required by your SNMPv3 configuration. |
The only difference between these protocols is the key extension algorithm used when an authentication hash is too short for the encryption key.
- AES-256 & AES-256-C: Function identically when paired with SHA-256 or stronger.
- AES-192 & AES-192-C: Function identically when paired with SHA-224 or stronger.
Summary: If the authentication protocol generates a long enough key (e.g., SHA-256 for AES-256), the standard and proprietary "-C" protocols are bit-for-bit the same. The "-C" logic only triggers when a "short" key must be stretched.
Auto-discovery
Click on “> Auto-discovery” and select EDFN Agent to configure IP ranges and other parameters.
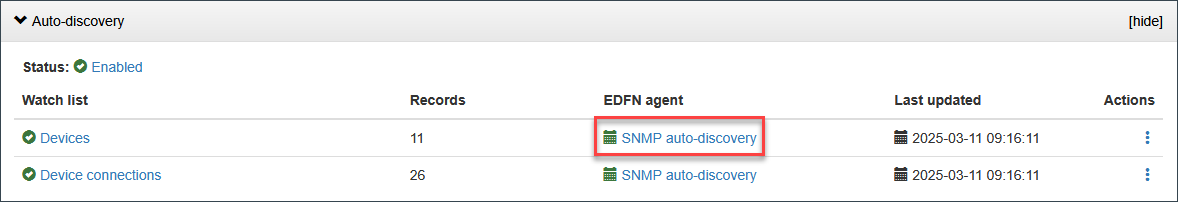
For detailed information, visit: > EDFN Administration Guide > EDFN Agents Configuration > Configuring Auto-Discovery Based on SNMP Polling.
SNMP Connectivity Tester
The SNMP Connectivity Tester is a utility used to verify that NFO can successfully reach and query a target network device using the specified credentials and settings. It is a critical troubleshooting step before adding a device to the main polling lists.
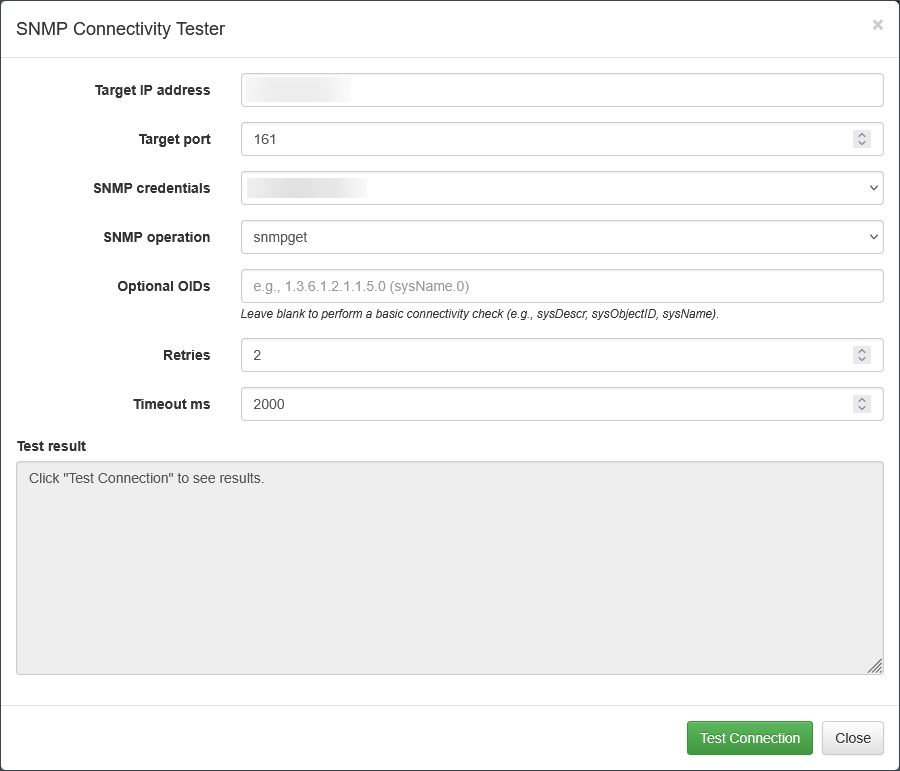
Using the Tester
The utility can be accessed via the SNMP Management interface. You must supply the necessary information for the test:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Target IP address | The IP address of the device you want to test. |
| Target port | The UDP port used for SNMP communication (default is 161). |
| SNMP credentials | Select a set of configured SNMPv2c or SNMPv3 credentials to use for the test. |
| SNMP operation | The SNMP command to execute. Options typically include snmpget (for a single OID) or snmpwalk (to traverse an OID tree). |
| Optional OIDs | Specify the OIDs you wish to query (e.g., sysName.0). Leave this field blank to perform a basic connection test, which often attempts to retrieve core system OIDs like sysDescr or sysName. |
| Retries | The number of times the tester should attempt the query if the initial attempt fails. |
| Timeout ms | The maximum time (in milliseconds) to wait for a response from the device before concluding the attempt has failed. |
After configuring the parameters, click "Test Connection" to view the results in the Test result box.
NFO Modules Using SNMP Data
10003: SNMP Information Monitor
When flow records are processed by NFO the Module queries this Service to get SNMP data, passing Exporter IP and Interface SNMP index as parameters. In its turn SNMP Service polls corresponding network device, using the Exporter IP/Management IP mapping, and caches this information, until it expires (Parameter: T - SNMP expiration time in secs).
For more information, see SNMP Information Monitor (10003 / 20003).
10103: SNMP Custom OID Sets Monitor
This Module enables you to create your own OIDs sets to report SNMP polling data.
Device group, introduced in NFO 2.8, allows you link OID sets specified in this Module with the Groups the device assigned to. For more information, see SNMP Custom OID Sets Monitor (10103 / 20103).
10700: SNMP Traps Monitor
This Module reports SNMP Traps. For more information, see SNMP Traps Monitor (10700 / 20700).
10701: Auto-discovery Reporter
This Module reports auto-discovered devices and device connections. For more information, see Auto-discovery Reporter (10701 / 20701 - 20702).
Suspending SNMP Polling from Inactive Devices
The success of SNMP polling and the subsequent data collection heavily rely on the availability and responsiveness of the polled devices. Depending on the device status and the specific OIDs queried, the following outcomes may occur:
| Potential issues | Output |
|---|---|
| Device is unresponsive | None. Check unresponsive devices on the NFO Status>Logs page or in the log file nfo_audit.log |
| Requested OID is not supported by the device | The OID is not included in the output |
| OID is returned, but the value is null | "MISSING" |
| Returned value is not valid, e.g. wrong type, lenth, etc. | "na" |
If a device is not responding to SNMP polling, the poling for this device is suspended for a period of time.
This period of time is set by the environment variable: NFO_SNMP_INACTIVE_POLL_TIMEOUT (default is 3600 seconds).
While a device is suspended, SNMP service requests for this device are skipped and counted in the number of SNMP polling skipped requests on the Status page.
When device is placed on "skip polling" list, an event log for this action is recorded in the nfo_audit.log file, which can be found in the$NFO_HOME/logs directory.
Here is an example:
2023-09-28 14:31:21,317 [NOTICE] -1: service=SNMP threadId=1 description="Unresponsive device" node=10.1.2.5:161 requestType=arbitrary resultCode=-1
2023-09-28 15:31:27,223 [NOTICE] -1: service=SNMP threadId=1 description="Unresponsive device" node=10.1.2.5:161 requestType=table(bulk) resultCode=-1
2023-09-28 16:33:31,644 [NOTICE] -1: service=SNMP threadId=1 description="Unresponsive device" node=10.1.2.5:161 requestType=arbitrary resultCode=-1
2023-09-28 17:33:37,441 [NOTICE] -1: service=SNMP threadId=1 description="Unresponsive device" node=10.1.2.5:161 requestType=arbitrary resultCode=-1
You may forward these logs to your SIEM system for active monitoring and alerting.
If you installed Splunk Universal Forwarder on NFO machine, here is the inputs.conf example:
[monitor:/opt/flowintegrator/logs/nfo_audit.log]
disabled = 0
index = flowintegrator
sourcetype = flowintegrator
_meta = nfo_hostname::nfo-server
Where nfo-server is NFO machine hostname.
Other Environment Variables
The environment variables available for further tuning SNMP polling and traps are described in the table below.
| Parameter | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| NFO_SNMP_REQ_QUEUE_LEN | SNMP requests (default and arbitrary) queue length | default=1000 (min – 100, max – 100000) |
| NFO_SNMP_TRAP_QUEUE_LEN | SNMP traps queue length | default=1000 (min – 100, max – 100000) |
| NFO_SNMP_TRAP_UNK_SEC_NAME_TIMEOUT | When a trap is received from a device with unconfigured credentials, the device is suspended for this period of time | default=600 seconds (min – 60, max – 86400) |
| NFO_SNMP_GETBULK_DISABLE | Disable GetBulk request for SNMP | default=0 enable getbulk, 1 - disable getbulk |
| NFO_SNMP_GETBULK_REPEATERS | SNMP max-repetitions count for GetBulk request | default=10 (min – 1, max – 100) |
| NFO_SNMP_MSG_MAX_SIZE | SNMP maximum message size (maxMsgSize) | default=0 (0 means that NetSNMP default value is used, which is 1500) (min - 484, max – 65507) |
| NFO_SNMP_RETRIES | SNMP retries count | default= -1 (-1 means that NetSNMP default value is used, which is 5) (min - 0, max – 10) |
| NFO_SNMP_INACTIVE_POLL_TIMEOUT | Period of time the poling for this device is suspended if device does not reply | default=3600 seconds |
| NFO_SNMP_THREAD_COUNT | The number of threads allocated for SNMP polling | Default=1 (min - 1, max - 1024) |
NFO server environment variables could be set here: Tracing and Configuration