Deployment with Splunk Enterprise
Combined indexer/search head
In single-instance Splunk Enterprise deployments, where one instance handles everything from input through indexing to search, NFO should be installed on a different server or virtual machine (VM) than the one on which the combined search head / indexer is installed. EDFN could be installed on the same server or VM on which NFO is installed or on a different one. This diagram shows where the processing components reside on the various processing tiers. This type of deployment is suitable for a department or a small enterprise.
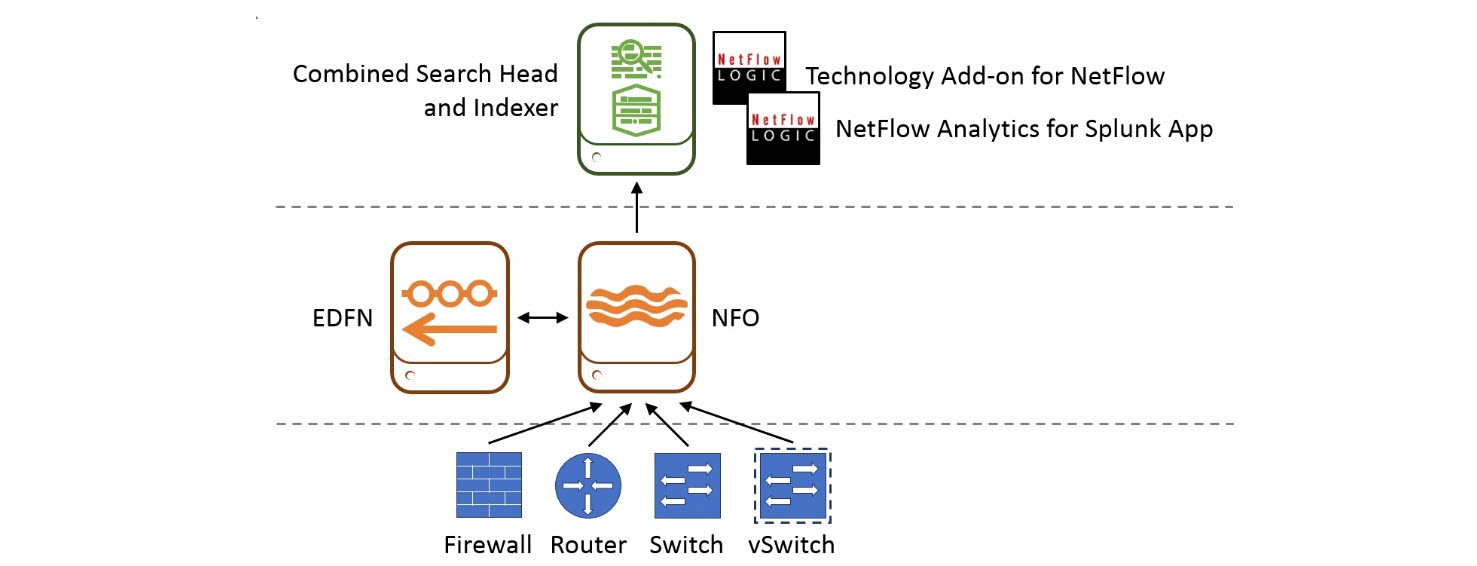
In this diagram, starting from the bottom up:
- Network device tier. Configure your routers, switches, firewalls, and virtual switches to send flow data to NFO.
- NFO / EDFN tier. NFO receives flow data, performs preprocessing and optimization, enriches it with external data provided by EDFN, and sends it to Splunk indexer for storage and indexing.
- Splunk tier. You need to install both Technology Add-on for Netflow (TA) and NetFlow Analytics for Splunk and other Apps here. TA defines all the necessary field names and tags for flow data to be CIM-compliant. The Apps provide dashboards, drill downs, searches, and alerting.
Separate Indexers, Search Heads, and Universal Forwarders
In distributed Splunk Enterprise deployments, you may add indexers and search heads to boost performance, and forwarders to ingest data. Typically, in these deployments, universal forwarder (UF) is the right choice. UF can be co-located on the machines that are generating data.
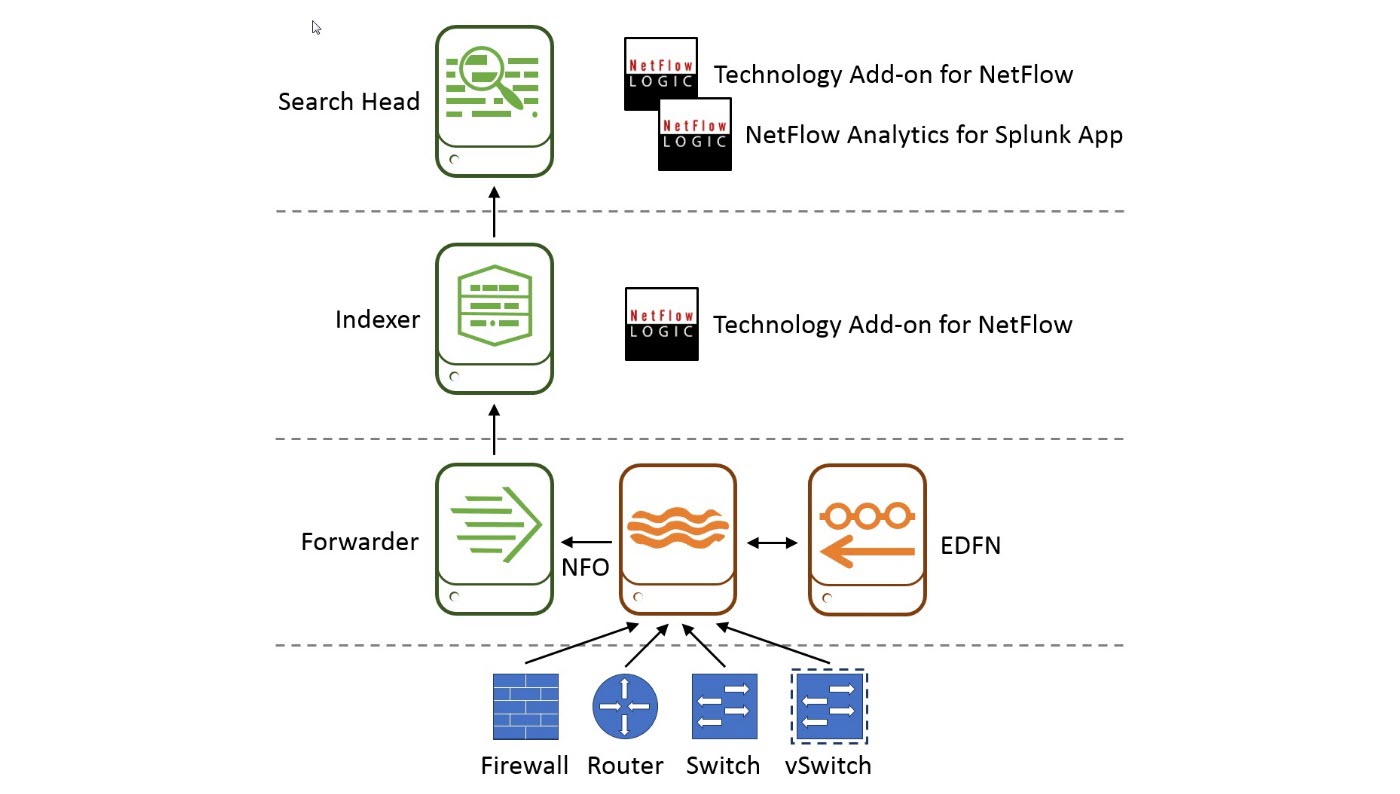
In this diagram, starting from the bottom up:
- Network device tier. Configure your routers, switches, firewalls, and virtual switches to send flows data to NFO. Picture firewall and vds
- NFO / EDFN /Splunk UF tier. NFO receives flow data, performs preprocessing and optimization, enriches it with external data provided by EDFN, and sends it to Splunk universal forwarder (UF). UF then forwards data to an indexer.
- Splunk indexing tier. Technology Add-on for Netflow (TA) is installed here. TA defines all the necessary field names and tags for flow data to be CIM-compliant.
- Splunk search head tier. You need to install both Technology Add-on for Netflow (TA) and NetFlow Analytics for Splunk and other Apps here. Note that you install the Technology Add-on for Netflow both here and in splunk indexing tier.
Multi-instance Indexers, Search Heads, Clusters, and Forwarders
In a large enterprise deployment you may have several search heads or a search cluster, several indexers or an index cluster, and many forwarders. You may also have an rsyslog or syslog-ng infrastructure for high availability ingestion of syslog data.
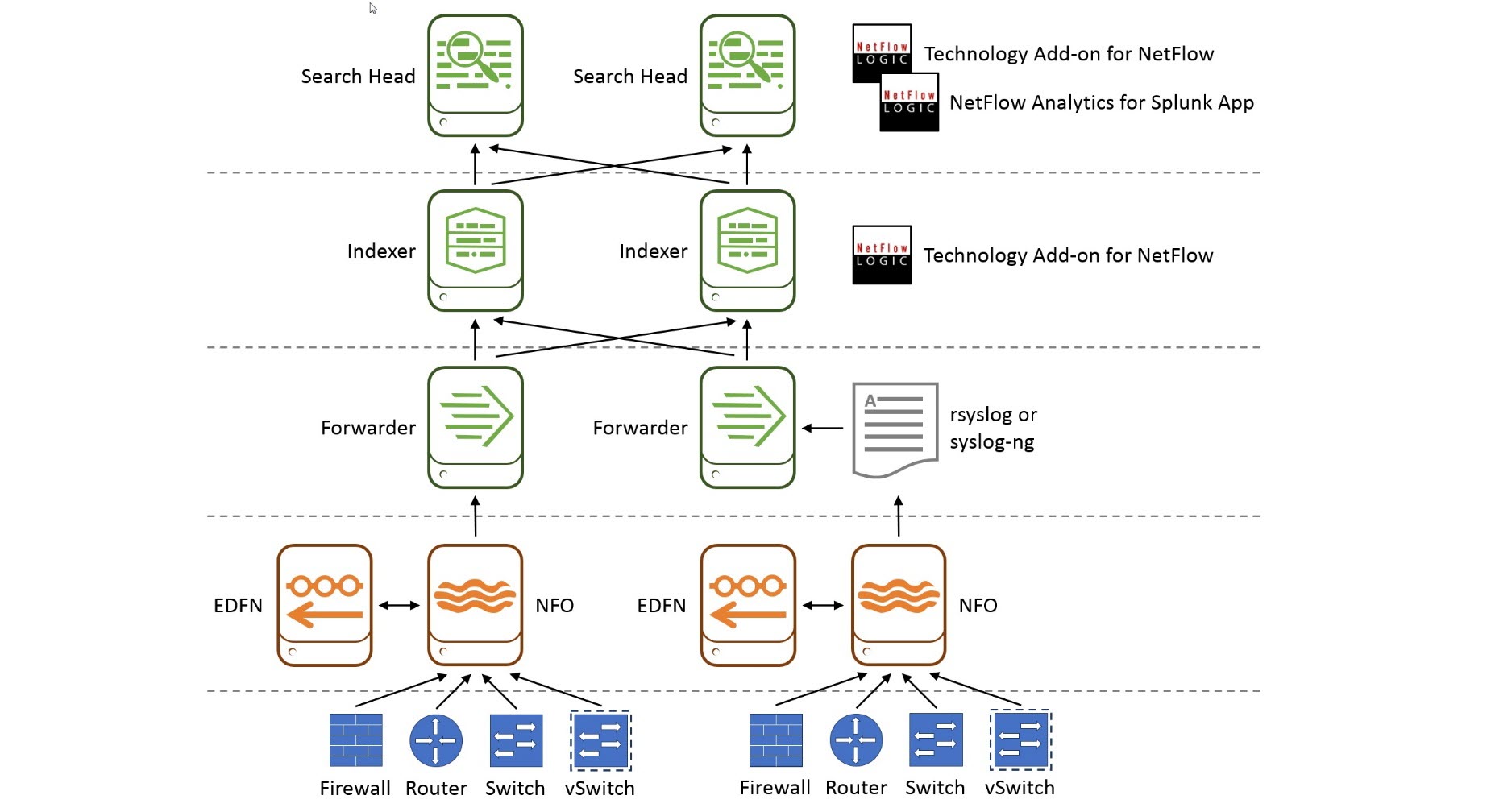
In this diagram, starting from the bottom up:
- Network device tier. Configure your routers, switches, firewalls, and virtual switches to send flows data to NFO.
- NFO / EDFN tier. NFO receives flow data, performs preprocessing and optimization, enriches it with external data provided by EDFN, and sends it to Splunk forwarder or rsyslog or syslog-ng.
- Splunk forwarder / rsyslog / syslog-ng tier. This is the data input for Splunk tier. In this tier you may have Splunk universal or heavy forwarders, and rsyslog / syslog-ng infrastructure.
- Splunk indexing tier. Technology Add-on for Netflow (TA) is installed here. TA defines all the necessary field names and tags for flow data to be CIM-compliant.
- Splunk search head tier. You need to install both Technology Add-on for Netflow (TA) and NetFlow Analytics for Splunk and other Apps here. Note that you install the Technology Add-on for Netflow both here and in splunk indexing tier.