Configure Splunk Inputs
This section guides you through configuring Splunk to receive NetFlow data from NetFlow Optimizer (NFO). You'll learn how to set up Splunk inputs depending on your deployment scenario.
There are four main options:
- Directly from NFO: Splunk can receive Syslogs directly from NFO on a specific UDP port.
- Using Splunk HEC: This option allows NFO to send data directly to Splunk using Splunk's HTTP Event Collector.
- Using a Universal Forwarder: This option involves installing a Universal Forwarder on a separate machine to collect NetFlow data and forward it to Splunk. The Universal Forwarder can either listen directly for NetFlow events or monitor log files created by syslog-ng or rsyslog.
- Using Splunk Connect for Syslog (SC4S): This option leverages SC4S as an intermediary to forward data between NFO and Splunk.
The following sections provide step-by-step instructions for configuring each option, including necessary Splunk configuration files and considerations for NetFlow data indexing.
Avalable SouceTypes
Choose the right source type for your data input and destination index.
-
flowintegrator: Use this source type if:
- Your input data format is either Syslog or JSON.
- The data is intended for an events-based index (stores detailed information about events).
-
netflow_metrics: Use this source type if:
- Your input data format is JSON.
- The data is intended for a metrics-based index (stores numerical data for analysis).
-
netflow_syslog_metrics: Use this source type if:
- Your input data format is Syslog.
- The data is intended for a metrics-based index.
Receiving Syslogs or JSON Directly from NFO (UDP port 10514)
Add the following lines to inputs.conf file and modify it for your netflow index, if necessary:
[udp://10514]
sourcetype = flowintegrator
index = flowintegrator
Configure Splunk HEC
For detailed instructions on configuring Splunk HEC, please visit: Getting Data In.
Configure Universal Forwarder
For detailed instructions on configuring Splunk UF, please visit: Forwarder Manual.
In general there are two options, either to listen directly for netflow events on a specific port or optionally to monitor files created by syslog-ng or rsyslog.
Configure Universal Forwarder to receive NFO data on a UDP port 10514
Create or modify %SPLUNK_HOME%/etc/system/local/inputs.conf file.
Add the following lines to inputs.conf file and modify it for your netflow index, if necessary:
[udp://10514]
sourcetype = flowintegrator
index = flowintegrator
Configure Universal Forwarder with syslog-ng or rsyslog
In this scenario syslog-ng or rsyslog are configured to listen to syslogs sent by NFO on a UDP port 10514. Syslog-ng or rsyslog are usually writing the logs into configurable directories. In this example we assume that those are written to /var/log/netflow.
Add the following lines to inputs.conf file and modify it for your netflow index, if necessary:
[monitor:///var/log/netflow]
sourcetype = flowintegrator
index = flowintegrator
It is very important to set sourcetype=flowintegrator and to point it to the index where Netflow Analytics for Splunk App and Add-on are expecting it.
Configure Universal Forwarder Output (Target Indexers)
During the installation of the Universal Forwarders a Receiving Indexer can be configured, as it can be seen here:
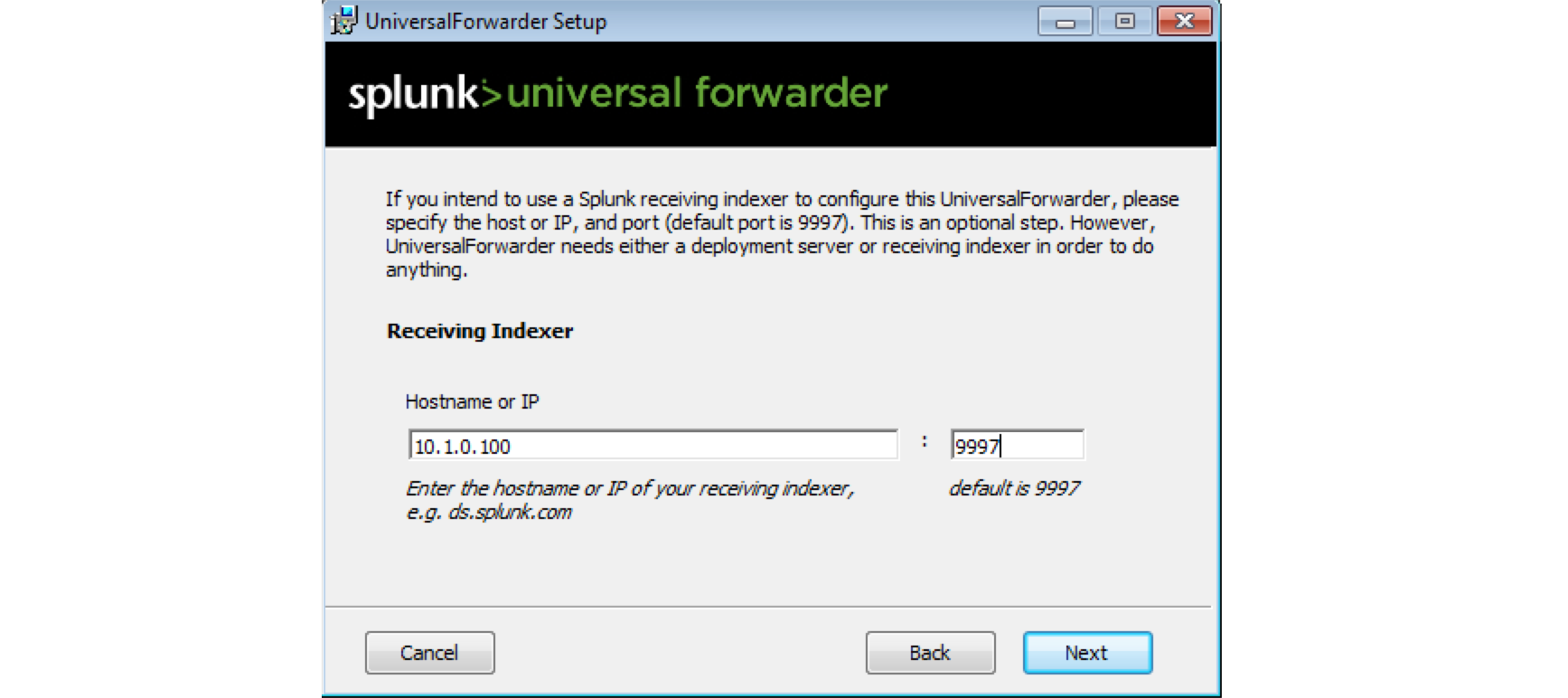
It is an optional step during the installation. If it was not configured or if load balancing is required, additional Receiving Indexers can be added later by adding to the %SPLUNK_HOME%/etc/system/local/outputs.conf file:
[tcpout]
defaultGroup = default-autolb-group
[tcpout:default-autolb-group]
server = 10.1.0.100:9997,10.1.0.101:9997
More info about load balancing: http://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/Forwarding/Setuploadbalancingd#How_load_balancing_works
To configure a universal forwarder to send data over HTTP, add an httpout stanza to the outputs.conf file on your universal forwarder.
Example httpout stanza:
[httpout]
httpEventCollectorToken = eb514d08-d2bd-4e50-a10b-f71ed9922ea0
uri = https://10.222.22.122:8088
For more details, visit Configure the universal forwarder to send data over HTTP.
Configure Splunk Connect for Syslog (SC4S)
You can use Splunk Connect for Syslog (SC4S) as a forwarder between NFO and Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud. This section describes how to install and configure SC4S and configure HTTP Event Collector (HEC).
Splunk HEC configuration
For details, visit Getting Data In.
SC4S Installation and Configuration
-
Install Docker Engine. For example, instruction for centos: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/centos/
-
Configure UDP receive buffer size and enable packet forwarding for IPv4. Edit
/etc/sysctl.conf:net.core.rmem_default = 17039360
net.core.rmem_max = 17039360
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 -
Save and apply to the kernel:
sysctl -p -
Do following steps for container and systemd configuration: https://splunk.github.io/splunk-connect-for-syslog/main/gettingstarted/docker-systemd-general/
-
Configure sc4s environment
/opt/sc4s/env_file:
SC4S_DEST_SPLUNK_HEC_DEFAULT_URL=https://<splunk_host>:8088
SC4S_DEST_SPLUNK_HEC_DEFAULT_TOKEN=<hec-token-value>
#Uncomment the following line if using untrusted SSL certificates
SC4S_DEST_SPLUNK_HEC_DEFAULT_TLS_VERIFY=no
SC4S_LISTEN_NETFLOWLOGIC_NFO_UDP_PORT=10514
-
Configure filter to distinguish NFO syslogs. Put following content into
/opt/sc4s/local/config/app_parsers/app-nfo.conffile:#
# Copyright (C) 2021 NetFlow Logic
# All rights reserved.
#
block parser nfo-parser() {
channel {
rewrite {
# set defaults these values can be overidden at run time by splunk_metadata.csv
r_set_splunk_dest_default(
index("flowintegrator")
source("sc4s:nfo")
sourcetype("flowintegrator")
vendor_product("netflowlogic_nfo")
template("t_msg_only")
);
# add nfo_hostname fields
set("${HOST}", value("fields.nfo_hostname"));
# remove nfc_id from the message
subst('nfc_id=(\d+) ', '', value("MESSAGE") flags(store-matches));
# add nfc_id field
set("$1", value("fields.nfc_id") condition("$1" ne ""));
};
};
};
application netflowlogic_nfo[sc4s-syslog] {
filter {
"${PROGRAM}" eq "NFO";
};
parser { nfo-parser(); };
}; -
Start SC4S:
systemctl start sc4s -
Configure NFO output:
<sc4s_host>:10514
Useful Commands
-
start/stop/restart SC4S:
systemctl start sc4ssystemctl stop sc4ssystemctl restart sc4s -
To check docker logs:
docker logs SC4S -
To validate SC4S status on Splunk side search following:
index=* sourcetype=sc4s:eventsindex=* sourcetype=sc4s:events "starting up" -
To find NFO syslogs:
index="flowintegrator" source="sc4s:nfo"