System Settings
Licensing
NFO requires a valid license to ingest, process, and export data. You can deploy NetFlow Optimizer as a standalone instance or as a Peer with NFO License Manager instance.
Apply a License
To apply a new license perform the following on the Licensing panel.
- Click on the
Browse...button - Select the license file
- Click Ok to apply the license
NFO License Manager Configuration
One of your NFO instances could be designated as a License Manager.
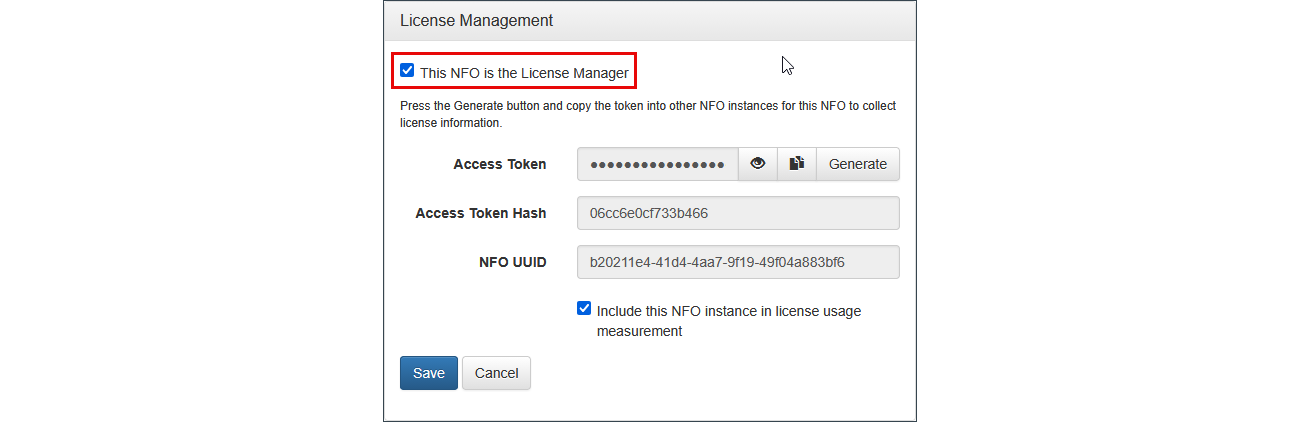
On this NFO instance perform the following:
- On License Management panel select checkbox
This NFO is the License Manager - Optionally deselect checkbox
Include this NFO license usage along with other NFO instancesif the License Manager usage should not be counted towards license usage, for example, when NFO is configured as a Repeater - Click
Savebutton - Press the
Generatebutton and copy the token into other NFO Peer instances for the NFO License Manager instance to collect license usage - Access Token is always shown, it can be copied at any time after generation. After first install, token and hash are empty. Token can be compared with NFO peer token using
Access Token Hashfield - Right panel “Measurement” shows License Usage information summary for all NFO peers per day. Detailed information per NFO may be downloaded in CSV format by pressing “Export license usage” link.
NFO License Manager checks license usage violations every midnight. Also it checks violations when tomcat service or NFO server is started/restarted.
NFO License Peer Configuration
Other NFO instances could be designated as NFO Peers.
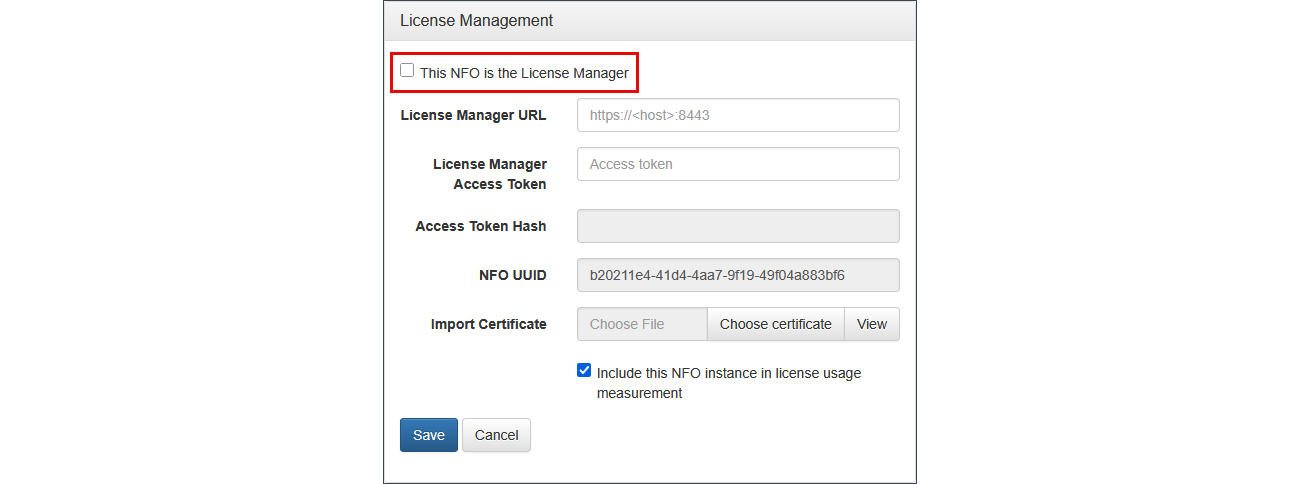
To configure NFO Peers perform the following:
-
On License Management panel checkbox
This NFO is the License Managerhas to be unchecked! -
Enter NFO License Manager URL:
<host>:<port>. For examplenfo-manager-host:8443, or<nfo-ip-address>:8443 -
Enter the License Manager token for access the License Manager
-
Click
Savebutton to apply changes -
After saving, the NFO Peer checks connection with NFO License Manager, request the license from it, and sends license usage information to it
-
For a secure connection between the NFO peer and the License Manager, the peer needs the License Manager's SSL/HTTPS certificate. This certificate is automatically stored during the first connection. However, if the certificate is updated on the License Manager, it must be manually imported.
- Navigate to NFO License Manager website.
- Click the lock icon to the left of the URL in the address bar to view site security information.
- Depending on your browser, select an option such as "Connection is secure," "Connection," or "View Certificate" to access the certificate details.
- Once the certificate viewer is open, navigate to a "Details" tab or similar section.
- Locate the option to save or export the certificate chain to a file. Choose a format like Base-64 encoded or X.509, and save the file to a location you can easily access.
- Return to the NFO peer and go to the Licensing section.
- Click
Choose certificate. - Select the certificate file you just downloaded. The NFO peer supports DER-encoded, Base64-encoded, or PKCS#7 X.509 certificates.
- To confirm the installation, click the “View” button to see the currently installed certificate.
The certificate is stored on the peer host at
${nfo_home}/tomcat/data/license_manager_truststore.jks.
- Click
- Navigate to NFO License Manager website.
-
Access token isn’t shown after saving, it can be compared with License Manager’s one using
Access Token Hashfield -
The right panel
Measurementshows License Usage only for this NFO peer
NFO peer checks license every midnight and updates it if it has been changed. Also at midnight NFO Peer sends its license usage to the License Manager.
License Usage
This section displays your NFO license usage, measured in blocks. For NetFlow, one block represents 1,000 flows per second, while for SNMP polling, one block accounts for 50 devices.
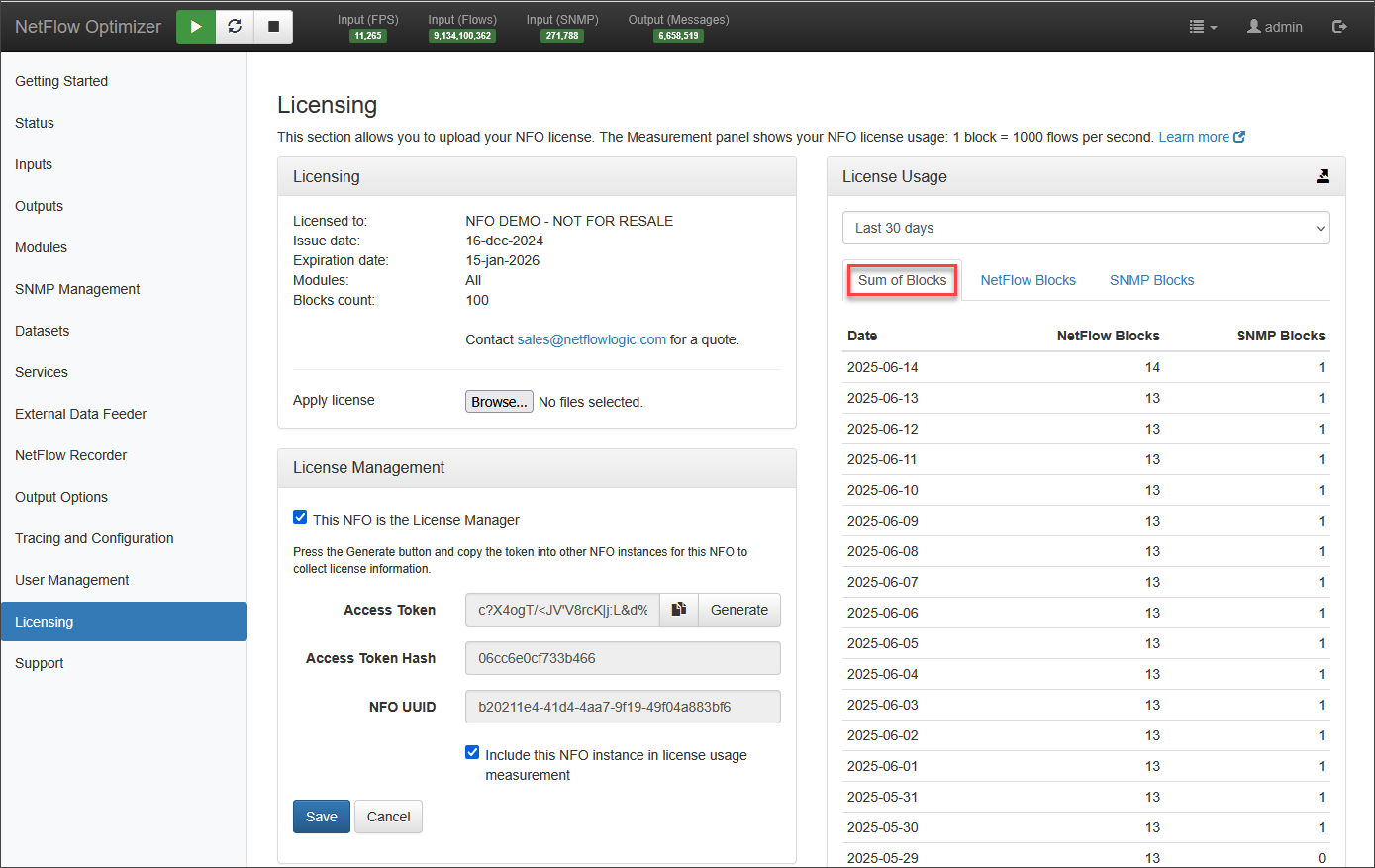
License usage has three tabs. The first tab, Sum of Blocks, shows the aggregated usage collected by the NFO license manager, covering both NetFlow and SNMP blocks. The NetFlow Blocks tab provides detailed NetFlow usage information broken down by NFO peers, while the SNMP Blocks tab shows SNMP polling usage for each NFO peer.
To learn more about NFO licenses and permitted overages, please refer to the End User License Agreement.
Server Parameters
There are several additional NetFlow Optimizer parameters located in <nfo_home>/server/etc/server.cfg file. You have to restart NetFlow Optimizer if you change them. Please contact us at https://www.netflowlogic.com/connect/support/ if you need assistance.
TRACE_ERR
LOG_DIR ..\..\logs
LOG_ROT_DIR ..\..\logs\bak
LOG_ROT_DAILY
LOG_COUNT 10
LOG_FILE_SIZE_KB 20000
SVR_ID NFI_SERVER
IT_RCVBUF 12582912
CONTROLLER_PORT 20047
CONFIG_PORT 20048
NF_PORT 9995
TIME_ZONE GMT
WT_COUNT 32
KT_COUNT 2
OT_COUNT 4
MAX_QOS_QSIZE 2000
THROTTLE_OUTPUT 0
THROTTLE_OUTPUT_RATE 1000
MODULES_OUTPUT JSON
REPLAY_OFD_OUTPUT JSON
High-Volume Processing (Linux Buffers)
Checking Packet Loss Due to Low Socket Buffers
In high-volume deployments you may experience UDP packets drops in the operating system socket buffers. They need to be large enough to handle the incoming and outgoing network traffic.
You can check if there are any packets lost on socket buffers in Linux kernel by execute the following command:
netstat -suna
Under Udp: section you should see:
xxxxxxxxxx packets received
xxxxxxxxxx packets to unknown port received.
xxxxxxxxxx packet receive errors
xxxxxxxxxx packets sent
0 receive buffer errors
0 send buffer errors
If you see high counters in receive or send buffer errors, please see sections below.
Input Buffer Settings (Linux)
The default Linux kernel settings are not sufficient for high-volume packet rate. This can lead to dropped packets and data loss. We recommend that you change both the receive buffer size in NFO and the socket read buffer size in Linux kernel.
To set the size of the receive buffer to <N> bytes in NFO, add the following string to <nfo_home>/server/etc/server.cfg:
IT_RCVBUF <N>
The valid values for parameter N are 124928 through 56623104. The default value is 12582912.
To set the size of the socket read buffer in Linux kernel to <N> bytes for current session, execute (under root privileges) the following command in a console:
sysctl -w net.core.rmem_max=<N>
To make this change persistent, do the following:
- Create a file with the arbitrary name, for example
nfo-custom.confin the directory/etc/sysctl.d:
touch /etc/sysctl.d/nfo-custom.conf
- Add the following string to the file:
net.core.rmem_max=<N>
- Run the following command to reload the settings from the file:
sysctl -p
- Restart the network service to update the system changes. The command depends on the Linux platform you are using.
To check what the socket read buffer size is currently used, execute the following command:
sysctl net.core.rmem_max
- NFO effectively uses the least size of those buffers.
- NFO Virtual Appliance has the socket read buffer size 12582912 -- the default value for NFO receive buffer.
Output Buffer Settings (Linux)
NFO may produce a lot of syslog/JSON messages, sometimes in bursts (at the end of data collection interval). This is especially true when Top N is set to 0 (meaning to send all messages), or when several NFO Outputs are configured. This could lead to packet drops on the way out with default Linux kernel settings. We recommend that you change default and maximum socket send buffer size in Linux kernel.
To set the size of the default socket send buffer in Linux kernel to <N> bytes for the current session, execute (under root privileges) the following command in the console:
sysctl -w net.core.wmem_default=<N>
To set the size of the maximum socket send buffer in Linux kernel to <N> bytes for the current session, execute (under root privileges) the following command in the console:
sysctl -w net.core.wmem_max=<N>
To make this change persistent, add the following string to /etc/sysctl.conf:
net.core.wmem_max=<N>
net.core.wmem_default=<N>
Then run the following command to reload the settings from the file:
sysctl -p
To check what the socket send buffer size is currently used, execute the following command:
sysctl net.core.wmem_default
Another way to reduce output packets loss on the socket buffers is to configure output throttling in NFO. To enable output throttling with rate N per second, add the following lines to<nfo_home>/server/etc/server.cfg:
THROTTLE_OUTPUT 1
THROTTLE_OUTPUT_RATE <N>
Security & HTTPS
This section describes how to install a certificate from a Certificate Authority into Tomcat. Self-signed certificate is already installed in $NFO_HOME/tomcat/conf/.tomcat_keystore, the keystore password is password and private key password is the same.
To change the default password, see Changing the Keystore Password section below.
If you want to replace self-signed certificate to a new one from a Certificate Authority, use following steps from https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/ssl-howto.html
HTTPS parameters are configured in the tomcat/conf/server.xml configuration file (Connector section). All Connector attributes are described here: https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/config/http.html. If keystore path or password are changed, corresponding Connector attributes should be modified.
Using your Existing Key and Signed Certificate
If you have the key and signed certificates, perform the following:
- Merge all certificates into a single file (chain):
cat tomcat.pem [intermediate.pem [intermediate-2.pem ... ]] root.pem > chain
- Convert the chain to a PKCS12 using OpenSSL:
openssl pkcs12 -export -in chain -inkey tomcat_key.pem -out .tomcat_keystore -name tomcat
- Validate .tomcat_keystore using keytool:
$NFO_HOME/java/jre/bin/keytool -list -v -keystore .tomcat_keystore
The output is expected like following:
Keystore type: PKCS12
Keystore provider: SUN
Your keystore contains 1 entry
Alias name: tomcat
Creation date: Jan 1, 2023
Entry type: PrivateKeyEntry
Certificate chain length: 3
Certificate[1]:
******* TOMCAT CERTIFICATE INFO IS HERE *******
Certificate[2]:
******* INTERMEDIATE CERTIFICATE INFO IS HERE *******
Certificate[3]:
******* ROOT CERTIFICATE INFO IS HERE *******
- Backup and replace $NFO_HOME/tomcat/conf/.tomcat_keystore with the new .tomcat_keystore using the following command:
cp .tomcat_keystore $NFO_HOME/tomcat/conf/.tomcat_keystore
Create a Local Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
If you don't have the key and signed certificate, follow these steps:
In order to obtain a Certificate from the Certificate Authority of your choice you have to create a so called Certificate Signing Request (CSR). That CSR will be used by the Certificate Authority to create a Certificate that will identify your website as "secure". To create a CSR follow these steps:
-
Delete preinstalled self-signed certificate:
-
Create a local Certificate:
$NFO_HOME/java/jre/bin/keytool -keysize 2048 -genkey -alias tomcat \
-ext "SAN=dns:${domain_name},ip:${host_ip}" \
-keyalg RSA -keystore $NFO_HOME/tomcat/conf/.tomcat_keystore
Where ${domain_name} is your server domain name and ${host_ip} is a host IP address. SubjectAlternativeName (SAN) and all its parts are optional. If host has different IP addresses or domain names, several comma separated dns:${domain_name} and ip:${host_ip} parts have to be added.
In some cases you will have to enter the domain of your website (i.e. www.domain.org) in the field "first- and lastname" in order to create a working Certificate.
- The CSR is then created with:
$NFO_HOME/java/jre/bin/keytool -certreq -keyalg RSA -alias tomcat \
-file certreq.csr -keystore $NFO_HOME/tomcat/conf/.tomcat_keystore
Now you have a file called certreq.csr that you can submit to the Certificate Authority (look at the documentation of the Certificate Authority website on how to do this). In return you get a Certificate.
Import the Certificate
Now that you have your Certificate you can import it into your local keystore. First of all you have to import a so called Chain Certificate or Root Certificate into your keystore. After that you can proceed with importing your Certificate.
- Download a Chain Certificate from the Certificate Authority you obtained the Certificate from.
For Verisign.com commercial certificates go to:
http://www.verisign.com/support/install/intermediate.html
For Verisign.com trial certificates go to:
http://www.verisign.com/support/verisign-intermediate-ca/Trial_Secure_Server_Root/index.html
For Trustcenter.de go to:
http://www.trustcenter.de/certservices/cacerts/en/en.htm#server
For Thawte.com go to:
http://www.thawte.com/certs/trustmap.html
- Import the Chain Certificate into your keystore
$NFO_HOME/java/jre/bin/keytool -import -alias root \
-keystore $NFO_HOME/tomcat/conf/.tomcat_keystore \
-trustcacerts -file <filename_of_the_chain_certificate>
- And finally import your new Certificate
$NFO_HOME/java/jre/bin/keytool -import -alias tomcat \
-keystore $NFO_HOME/tomcat/conf/.tomcat_keystore \
-file <your_certificate_filename>
If signed certificate is imported successfully, you will see this message: "Certificate reply was installed in keystore".
Import the Certificate into External Data Feeder for NFO (EDFN)
You must import the certificate into EDFN truststore. Please see Import the Certificate into External Data Feeder for NFO truststore in EDFN Administration Guide.
Changing the Keystore Password
This section outlines the procedure for updating the keystore passwords used by the Tomcat server for NetFlow Optimizer (NFO).
Prerequisites
- Administrative access to the server where NFO is installed.
- Knowledge of the current keystore passwords. Default passwords are
password.
- Backup: Before making any changes, it is highly recommended to create a backup of both the
.tomcat_keystore,.truststore, andserver.xmlfiles in/opt/flowintegrator/tomcat/congdirectory. - Consistency: Ensure that the new passwords in the
server.xmlfile exactly match the passwords you set usingkeytool.
Instructions
-
Navigate to the Tomcat configuration directory:
cd /opt/flowintegrator/tomcat/conf/ -
To change the password for the
.tomcat_keystore, use thekeytoolcommand. You will be prompted to enter the current password and then the new password./opt/flowintegrator/java/jre/bin/keytool -storepasswd -keystore .tomcat_keystoreNote: Since the
.tomcat_keystoreis in the PKCS12 format, the keystore password and the key password are the same. You do not need to change them separately. -
Similarly, change the password for the
.truststoreusingkeytool. You will be prompted for the current and new passwords./opt/flowintegrator/java/jre/bin/keytool -storepasswd -keystore .truststore -
Update the
server.xmlfile to reflect the new passwords. Open the file for editing:vi server.xml -
Change flowintegrator/tomcat/conf/server.xml attributes truststorePassword, certificateKeystorePassword, and certificateKeyPassword to your new password.
-
Save the
server.xmlfile and exit the editor. -
Restart the Tomcat service for the changes to take effect.
- On Linux, use the appropriate command for your system (e.g.,
systemctl restart tomcat_nfo.service). - On Windows, restart the
NFOSvcservice.
- On Linux, use the appropriate command for your system (e.g.,
Tracing & Maintenance
The Tracing and Configuration tab provides tools for system health, log management, and configuration persistence.
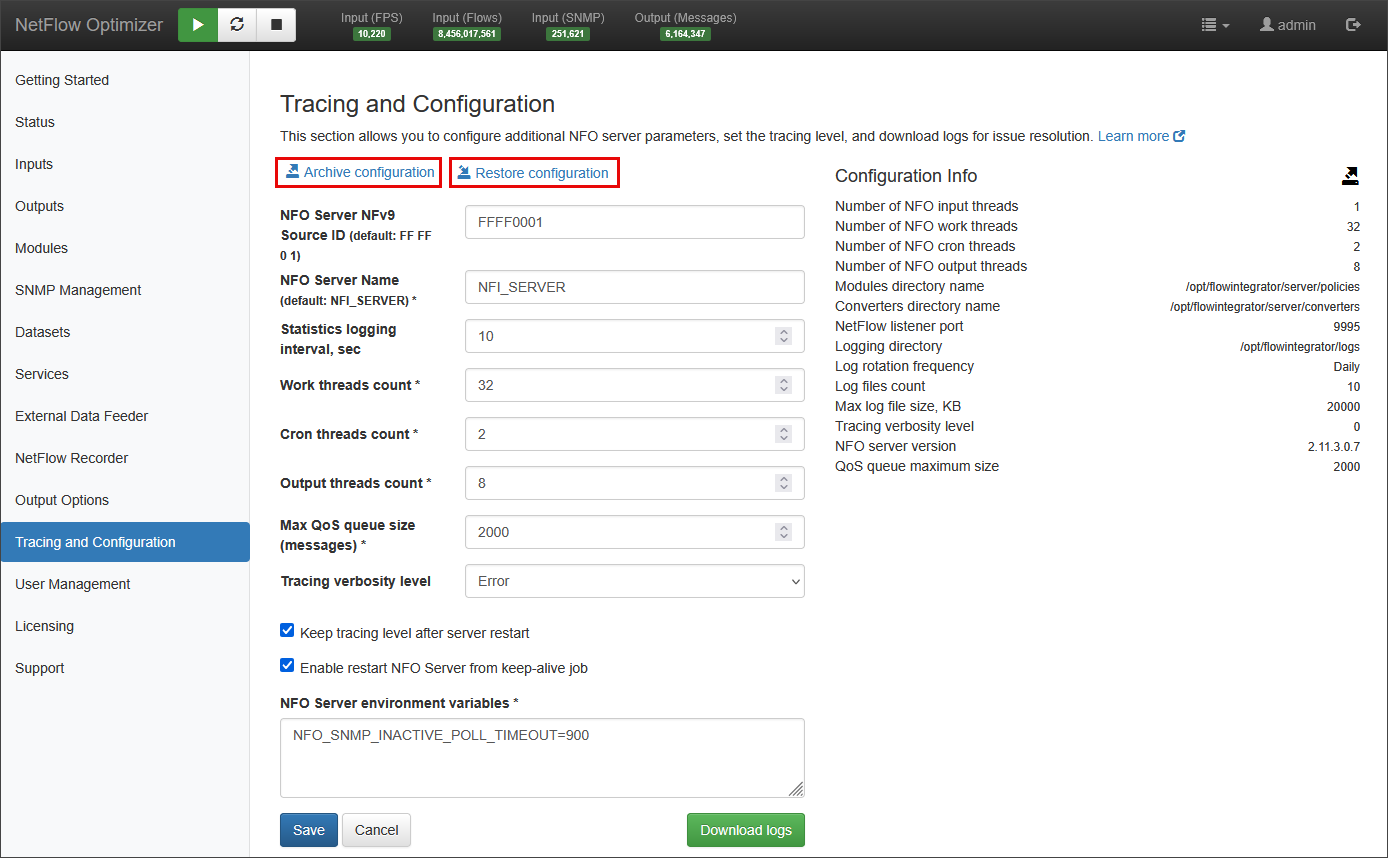
Archive/Restore Configuration
"Archive configuration" zips all NFO configuration files and stores them on a local drive (the file name and path will be displayed). To restore the configuration, you need to move this file to your desktop (or any folder on your computer) and press "Restore configuration". This will open a dialog to upload the ZIP file. Note that for security reasons, we do not automatically save the zipped configuration to your computer.
This method is the standard for synchronizing logic and parameters across a distributed environment. It ensures that all peers in a cluster are processing data with identical rules and modules.
This is the recommended method for adding new Peers to your cluster. Instead of manually configuring each node, use the following workflow to ensure consistency:
- Configure Peer 1: Set up all required Logic Modules and parameters on your first peer node.
- Create Archive: Use the Archive function on Peer 1 to generate a configuration backup.
- Deploy Peers 2, 3, 4+: * Install a fresh NFO instance on the new machine.
- Use the Restore function to apply the archive from Peer 1.
- Once restored, join the instance to NFO Central.
Using this approach ensures that all peers operate as identical "processing units" without the risk of human error during manual setup.
Automating Configuration Archival
You can schedule periodic configuration backups without using the NFO GUI by utilizing the API script below.
#!/bin/bash
# NFO host
NFO_HOST=localhost
# NFO port
NFO_PORT=8443
# NFO admin account password
NFO_ADMIN_PASSWORD='changeme'
# -----------------------------
# If NFO version >= 2.11.1, the CSRF token is required
# for HTTP request types: POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE.
# For exampe:
# -H 'X-XSRF-TOKEN:QQA=' --cookie 'XSRF-TOKEN=A'
# -----------------------------
# loging
LOCATION=$(curl -si -d 'j_username=admin' --data-urlencode "j_password=${NFO_ADMIN_PASSWORD}" \
-H 'X-XSRF-TOKEN:QQA=' --cookie 'XSRF-TOKEN=A' \
-c cookies \
--insecure \
"https://${NFO_HOST}:${NFO_PORT}/j_security_check" \
| grep -i "Location:" | awk '{print $2}' | tr -d '\r')
if [ "$LOCATION" != "/" ]; then
echo "Invalid credentials"
exit 1
fi
# dump config into /opt/flowintegrator/conf-backup/nfo_cfg_*.zip
curl -H 'Accept:application/json' -b cookies --insecure \
"https://${NFO_HOST}:${NFO_PORT}/nfirapi/admin/config"
# logout
curl --insecure -X POST -H 'X-XSRF-TOKEN:QQA=' --cookie 'XSRF-TOKEN=A' -b cookies "https://${NFO_HOST}:${NFO_PORT}/logout"
echo ""
# remove cookies file
rm cookies
Parameters
- NFO Server NFv9 Source ID: a unique identifier used to distinguish the NFO server when it forwards NetFlow v9 messages. This ID is included in the header of every NetFlow v9 packet generated by NFO.
- NFO Server Name: a unique, user-defined name to the NetFlow Optimizer (NFO) instance.
- Statistics logging interval: specifies how frequently, in seconds, the NFO's operational statistics are logged and refreshed on Status page.
- Work threads count: specifies the number of parallel threads that the module uses to process incoming data. Increasing this count can improve performance by allowing NFO to handle more data concurrently.
- Cron threads count: specifies the number of parallel threads dedicated to executing scheduled tasks (cron jobs runniing at the end of data collection intervals).
- Output threads count: specifies the number of parallel threads that the module uses to format and send data to configured outputs. Increasing this count can enhance the throughput of data leaving the module, which is particularly useful for handling a high volume of output data.
- Max QoS queue size (messages): sets the maximum number of messages that the Quality of Service (QoS) queue can hold. When this limit is reached, any new incoming messages that are subject to QoS rules will be dropped. This parameter helps prevent the system from becoming overloaded by limiting the amount of buffered data.
- Tracing verbosity level: this drop-down controls the amount of detail included in the NFO's log files. A higher verbosity level provides more detailed information for debugging and troubleshooting, while a lower level reduces log volume for normal operations. The logging levels are (from least to most verbose): Error, Debug, Verbose, Flood.
You can also set NFO environment variables here.
| Parameter | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| NFO_SNMP_REQ_QUEUE_LEN | SNMP requests (default and arbitrary) queue length | default=1000 (min – 100, max – 100000) |
| NFO_SNMP_TRAP_QUEUE_LEN | SNMP traps queue length | default=1000 (min – 100, max – 100000) |
| NFO_SNMP_TRAP_UNK_SEC_NAME_TIMEOUT | When a trap is received from a device with unconfigured credentials, the device is suspended for this period of time | default=600 seconds (min – 60, max – 86400) |
| NFO_SNMP_GETBULK_DISABLE | Disable GetBulk request for SNMP | default=0 enable getbulk, 1 - disable getbulk |
| NFO_SNMP_GETBULK_REPEATERS | SNMP max-repetitions count for GetBulk request | default=10 (min – 1, max – 100) |
| NFO_SNMP_MSG_MAX_SIZE | SNMP maximum message size (maxMsgSize) | default=0 (0 means that NetSNMP default value is used, which is 1500) (min - 484, max – 65507) |
| NFO_SNMP_RETRIES | SNMP retries count | default= -1 (-1 means that NetSNMP default value is used, which is 5) (min - 0, max – 10) |
| NFO_SNMP_INACTIVE_POLL_TIMEOUT | Period of time the poling for this device is suspended if device does not reply | default=3600 seconds |
| NFO_SNMP_THREAD_COUNT | The number of threads allocated for SNMP polling | Default=1 (min - 1, max - 1024) |
Restart NetFlow Optimizer for the changes to take effect