NFO Central
The NFO Central is the central configuration hub for managing distributed NetFlow Optimizer deployments. It allows you to define a node's operational role and manage the connection and intelligent load distribution across multiple NFO instances.
NFO Central and distributed deployment functionality are currently available only for Linux-based NFO installations. Windows deployments currently support Standalone mode only.
The three primary operational modes are:
- Standalone: A single NFO instance handling all functions.
- NFO Central: The dedicated control plane for managing peer connections, licensing, and intelligent traffic distribution.
- NFO Peer: A worker node that receives flow data and configuration from the NFO Central instance.
Configuring Standalone Node

In this mode, the node functions as a single, all-in-one instance where all collection, processing, and output tasks are handled by one server without external peer distribution.
Configuring a Distributed Deployment
Setting up a distributed NFO architecture involves the following steps:
- Deploy NFO Central Node and generate a secure access token.
- Deploy two or more NFO Peer Nodes to act as workers.
- Enter the generated token into each NFO peer node to establish authentication and connection.
- Verify peer connectivity within the NFO Central management interface.
- Create a Peer Pool under the Load Balancer settings.
- Assign Peer nodes to the pool to begin intelligent traffic distribution.
Configuring NFO Central (The Control Plane)
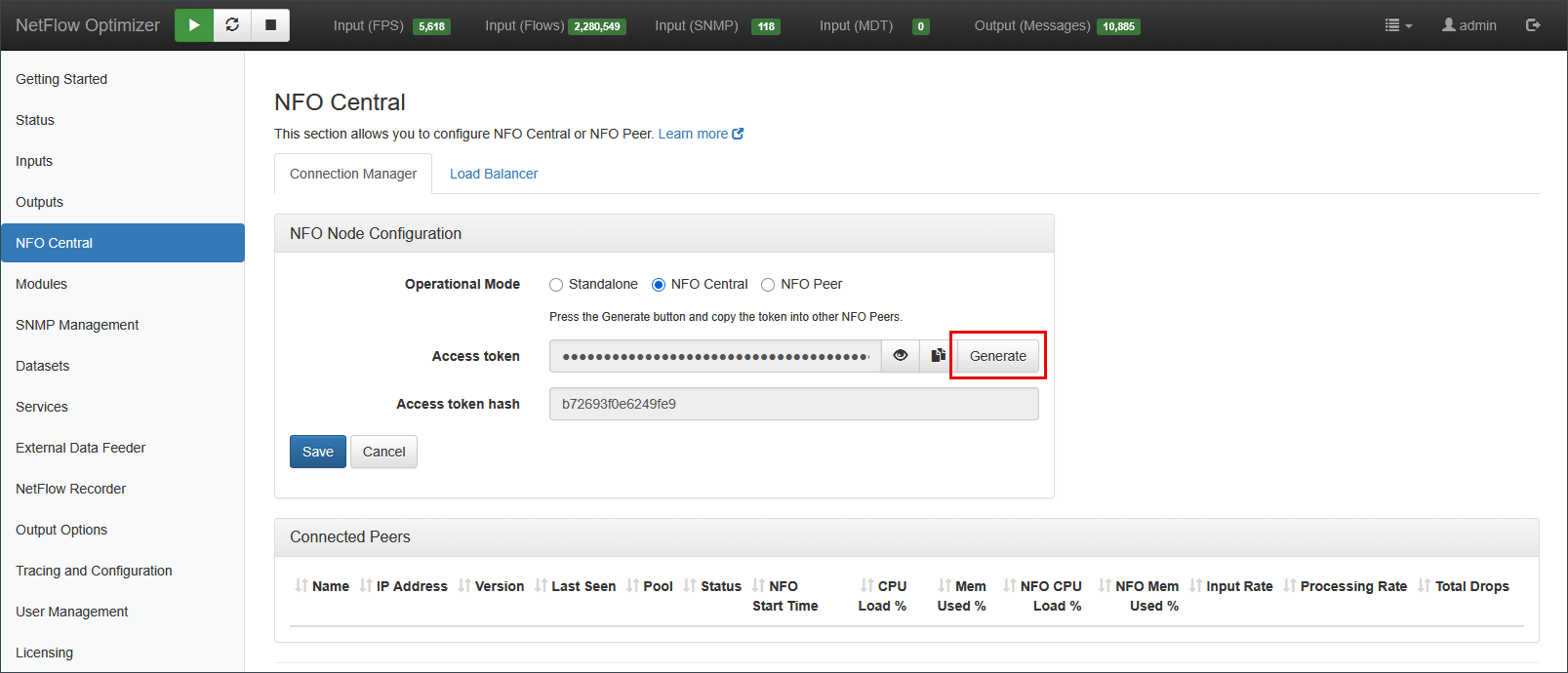
When selecting the NFO Central operational mode, the interface expands to provide authentication tokens used to secure communication with peer nodes.
- Access Token: A token generated by NFO Central that NFO Peers use to authenticate their connection. Press the Generate button to create a new token.
- Access Token Hash: A secure hash of the access token, displayed for verification purposes.
- Connected Peers: A list showing all peer nodes that have successfully connected to this NFO Central instance, including their status, performance metrics, and data rates.
The Connected Peers table provides essential real-time monitoring statistics for load balancing and health checking:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The hostname of the connected NFO Peer node. |
| IP Address | The network address of the connected NFO Peer node. |
| Version | The software version running on the NFO Peer node. |
| Last Seen | Timestamp of the last successful communication with the peer. |
| Pool | The name of the NFO Peer Pool. |
| Status | Shows the current operational state (e.g., ONLINE, OFFLINE). |
| NFO Start Time | The timestamp indicating when the NFO Peer process was last started. |
| CPU Load % | The current system-wide CPU utilization for the peer node. |
| Mem Used % | The percentage of system memory currently utilized by the peer node. |
| NFO CPU Load % | The percentage of CPU dedicated specifically to the NFO process on the peer node. |
| NFO Mem Used... | The amount of memory being used specifically by the NFO process. |
| Input Rate | The number of packets/messages the peer is currently ingesting. |
| Processing Rate | The rate at which the peer is processing flows, typically measured in flows per second. |
| Total Drops | The cumulative number of flows dropped by the peer node due to overload or processing issues. |
Configuring NFO Peer (The Worker Node)
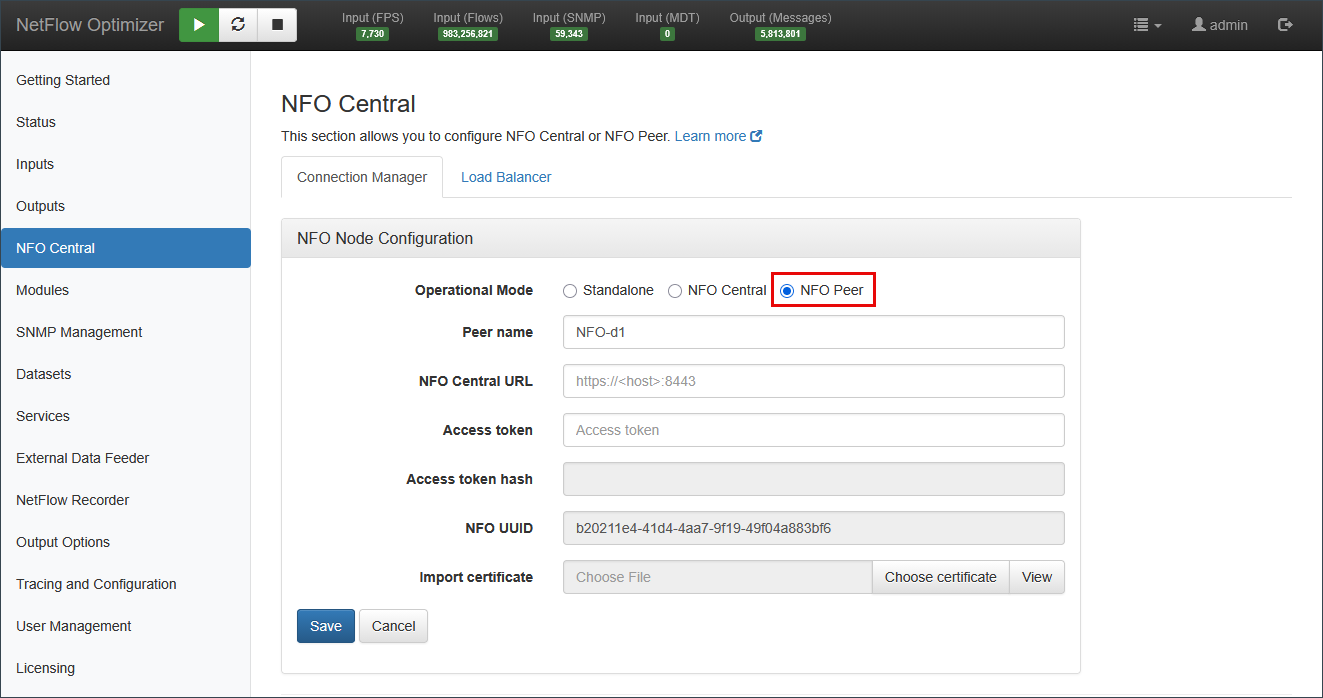
When setting a node to the NFO Peer operational mode, you must specify the connection details for the central management hub.
- Peer name: The unique name of the peer node within the deployment.
- NFO Central URL: The full URL (including port) of the central control plane instance (e.g.,
https://<host>:8443). - Access Token: The access token generated by the NFO Central instance, used by the peer to authenticate its connection.
- Access token hash (Read-Only): A secure hash of the access token.
- NFO UUID (Read-Only): The unique identifier for the NFO instance.
- Import certificate: Used to secure the connection between the peer and NFO Central.
Verify Peer Connectivity
To ensure your distributed environment is operational, navigate to the Connection Manager tab on the NFO Central instance to review the Connected Peers table
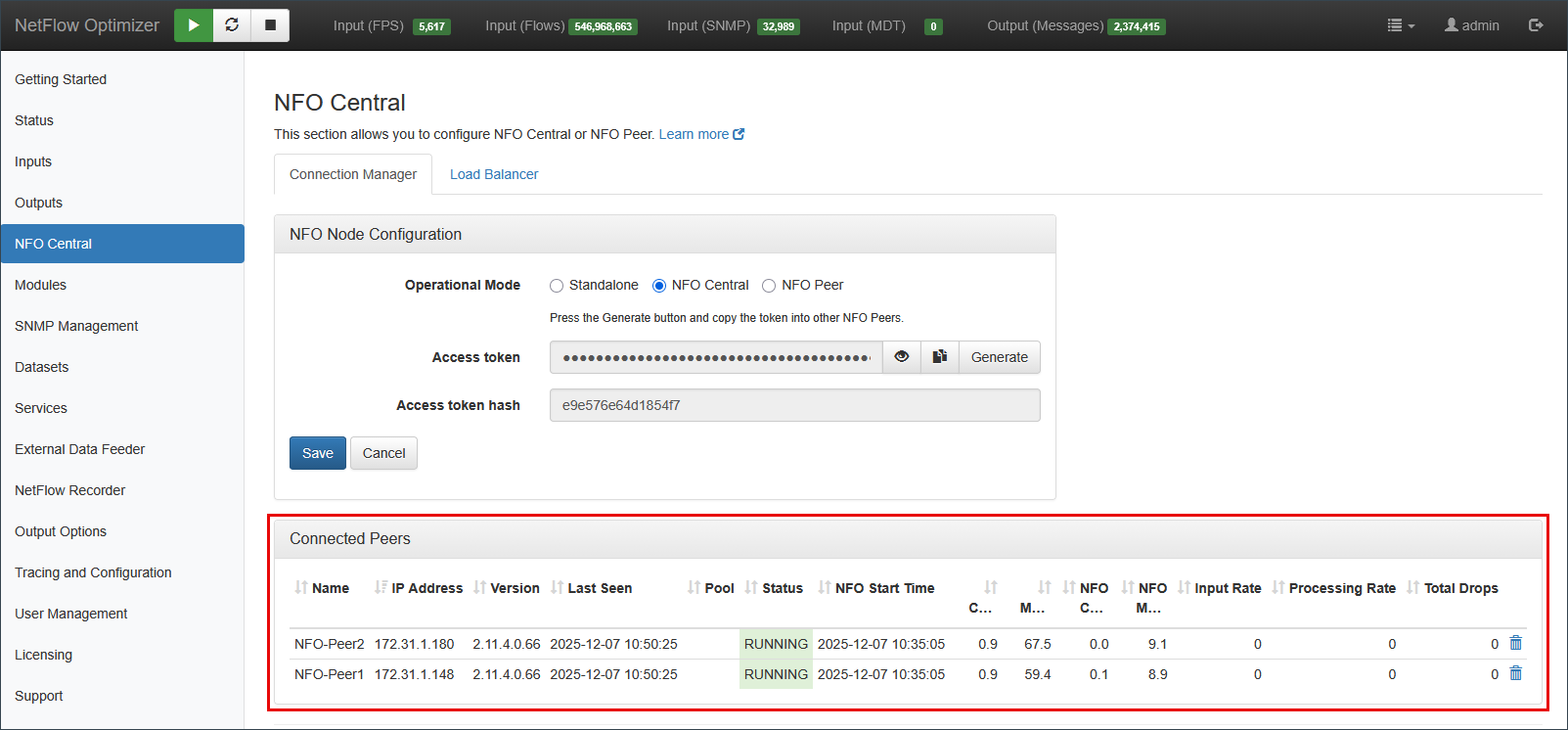
This real-time dashboard provides a comprehensive list of all linked worker nodes, such as NFO-Peer1 and NFO-Peer2.
- Operational Status: Confirm that the Status column displays RUNNING in a green highlight for each active peer, which indicates a healthy connection.
- Connection Timing: Monitor the Last Seen column to view the timestamp of the most recent communication between NFO Central and the peer node.
- System Health: View real-time system resource utilization, including CPU Load % and Mem Used %, to identify if any peer is reaching hardware limits.
- Data Throughput: Review the Input Rate and Processing Rate to verify that flow records are being successfully ingested and handled across the architecture.
- Stability Monitoring: Track the Total Drops column; a high cumulative count of dropped flows may indicate a node overload requiring a pool rebalance.
Once peer connectivity is verified, you can proceed to the Load Balancer tab to create a Peer Pool and assign these nodes for distributed processing.
Steps to Assign Peers to a Pool
To finalize the distributed configuration, you must organize your verified peers into logical groups known as Peer Pools. This structure allows NFO Central to distribute the data load across multiple nodes simultaneously.

- Create the Pool: Navigate to the Load Balancer tab on the NFO Central interface. Click the Create New Pool button to launch the pool definition window.

- Define the Pool Name: In the configuration popup, enter a clear and descriptive Name for the pool (e.g.,
My-Pool1). - Select Peers: Use the Select peer to add... dropdown menu to view the list of verified peer nodes that have successfully connected to NFO Central.
- Add and Assign: Select the desired peer (e.g.,
NFO-Peer1) and click the Assign button next to the dropdown to move the peer node into the new pool. - Finalize Configuration: Once all required peers are listed in the assignment window, click Save to confirm the pool creation.
After the pool is saved, NFO Central will begin distributing traffic from your exporters to the peers within that pool, dynamically balancing the load based on real-time ingestion rates.
Configuring the Rebalancing Interval
To fine-tune how NFO Central manages load distribution, you can configure the Rebalancing time interval (sec) located within the Load Balancer tab.
- Default Setting: The rebalancing interval is set to 90 seconds by default.
- Function: This variable dictates how frequently NFO Central monitors the input packets rate per device to determine if exporters should be shifted between peer nodes to balance the load.
- Adjustment: You can use the selector in the Load Balancer tab to increase or decrease this value based on your network's traffic volatility.
For optimal performance, it is recommended to set this interval to three times the data collection interval used in your logic modules (such as those configured for aggregation or volume reduction). This ensures that the rebalancing logic has sufficient historical data to make informed distribution decisions without reacting to transient traffic spikes and provides the optimal balance between responsive load shifting and reliable data aggregation.